Georg Eide convicted for having aided cash buyer in attempt to illegally export toxic ship
Last Friday, the Sunnhordland District Court in Norway sentenced ship owner Georg Eide to six months unconditional imprisonment for having assisted scrap dealer Wirana in an attempt to illegally export the TIDE CARRIER (aka EIDE CARRIER and HARRIER) to Pakistan for scrapping. The Court also ordered the confiscation of criminal dividends of NOK 2 million from Eide Marine Eidendom AS.
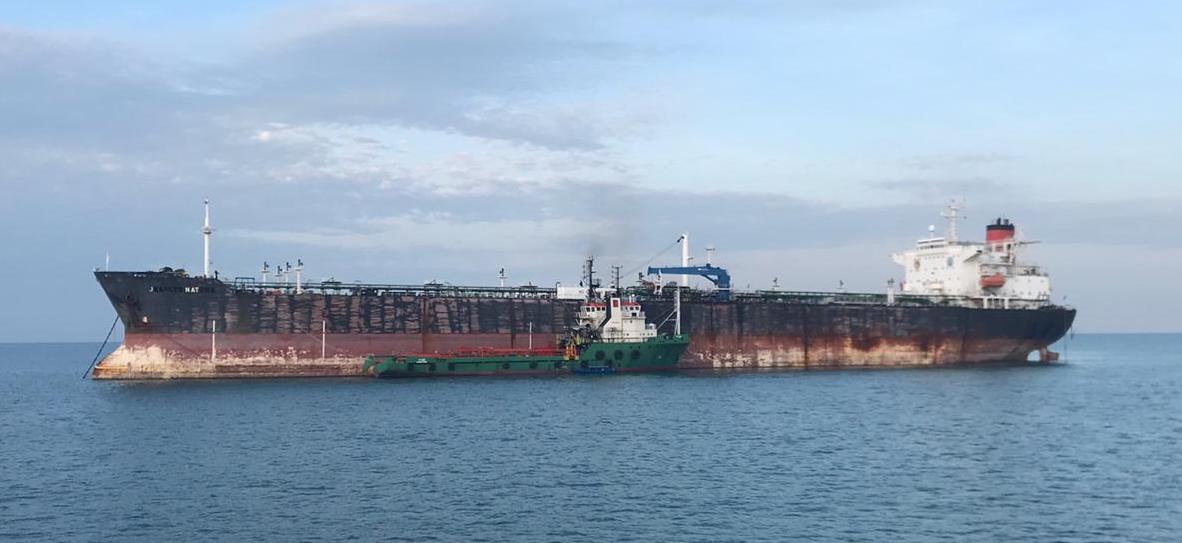
After a decade in lay-up in Norway, the TIDE CARRIER was sold to one of the most well-known cash buyers, Wirana. The intent was to scrap the ship on the beach of Gadani in Pakistan. The NGO Shipbreaking Platform, together with its member organisation Bellona, tipped the police about the imminent illegal export in February 2017. The vessel was arrested upon finding onboard a “last voyage for breaking in Pakistan insurance” issued by Skuld Maritime Agency and two certificates issued on the same day by Marine Warranty Surveyor Aqualis Offshore - one for a voyage with the purpose of refurbishment work in Dubai and one for a last voyage to the scrap yards in Pakistan [1].

Waste exports are strictly regulated in Norwegian, European and international law. The purpose is to protect developing countries from the dumping of hazardous wastes and the harm caused to workers, surrounding communities and the environment when toxics are not treated in an environmentally sound manner. Ships contain numerous toxic materials such as asbestos, heavy metals in paints and residue oils. Last year, the Basel Convention Ban Amendment entered into global force, banning the export of hazardous wastes, including end-of-life ships, from OECD to non OECD countries. The EU transposed the Ban Amendment into EU Law in 1997.
Waste trafficking linked to shipbreaking is being investigated by enforcement authorities in several EU Member States. It is also being looked at from a transnational point of view via Europol and Interpol. The Norwegian District Court emphasised an increasing need to counter environmental crime. Public Prosecutor Maria Bache Dahl and the judges stressed that there was no doubt that Eide had knowledge that the ship would be scrapped in Asia, and had also provided assistance in preparing for its last voyage [2].
Eide may appeal the verdict.
NOTES
[1] For more details on the case, see “The controversial case of the Harrier”.
[2] In 2019, separate action was taken against cash buyer Wirana who was fined NOK 7 million for having falsified papers to deceive Norwegian authorities about the ship's true destination and its seaworthiness to allow the vessel to leave Norway. Earlier this year, the public prosecutors’ office dismissed the charge and withdrew the penalty charge notice issued to MWS Aqualis Offshore AS for undisclosed reasons.