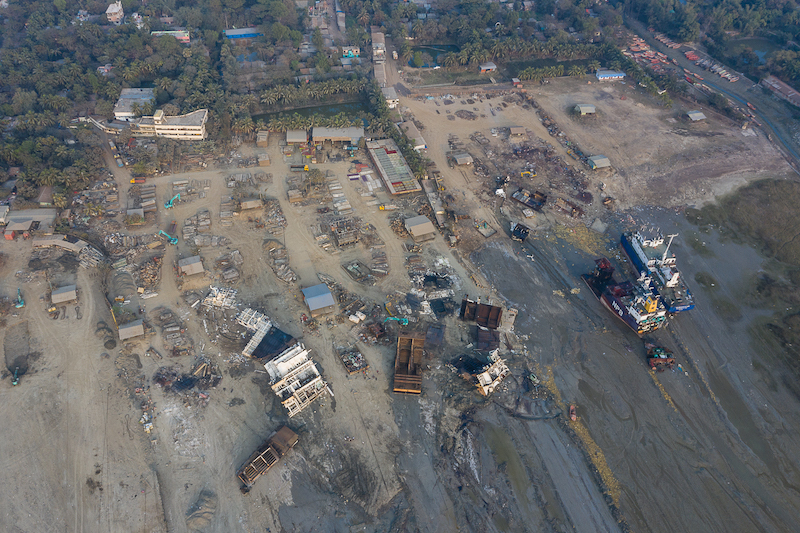
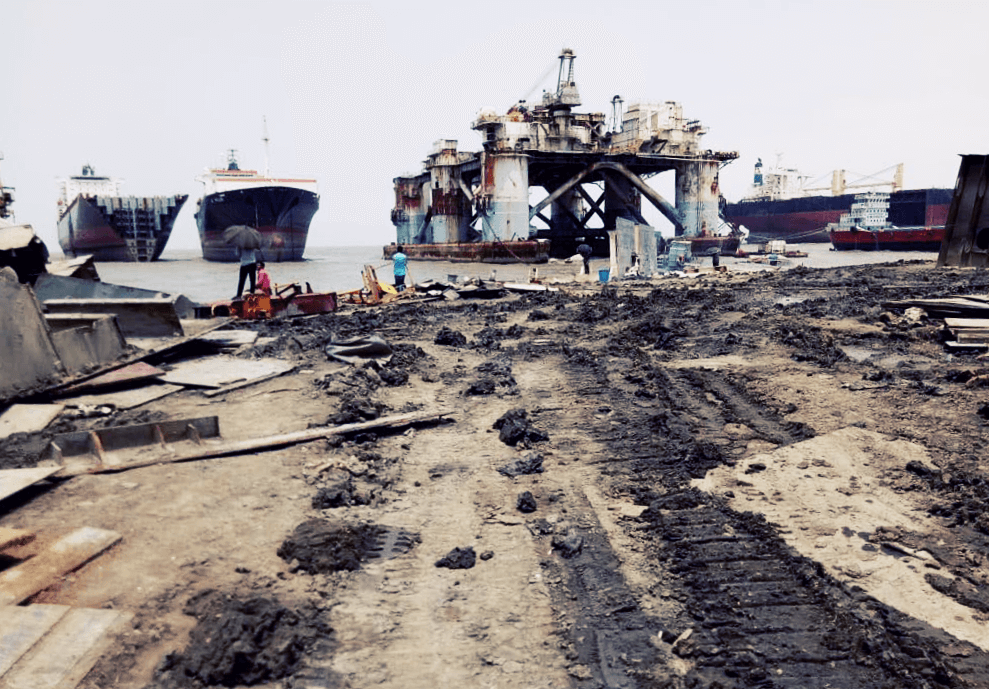
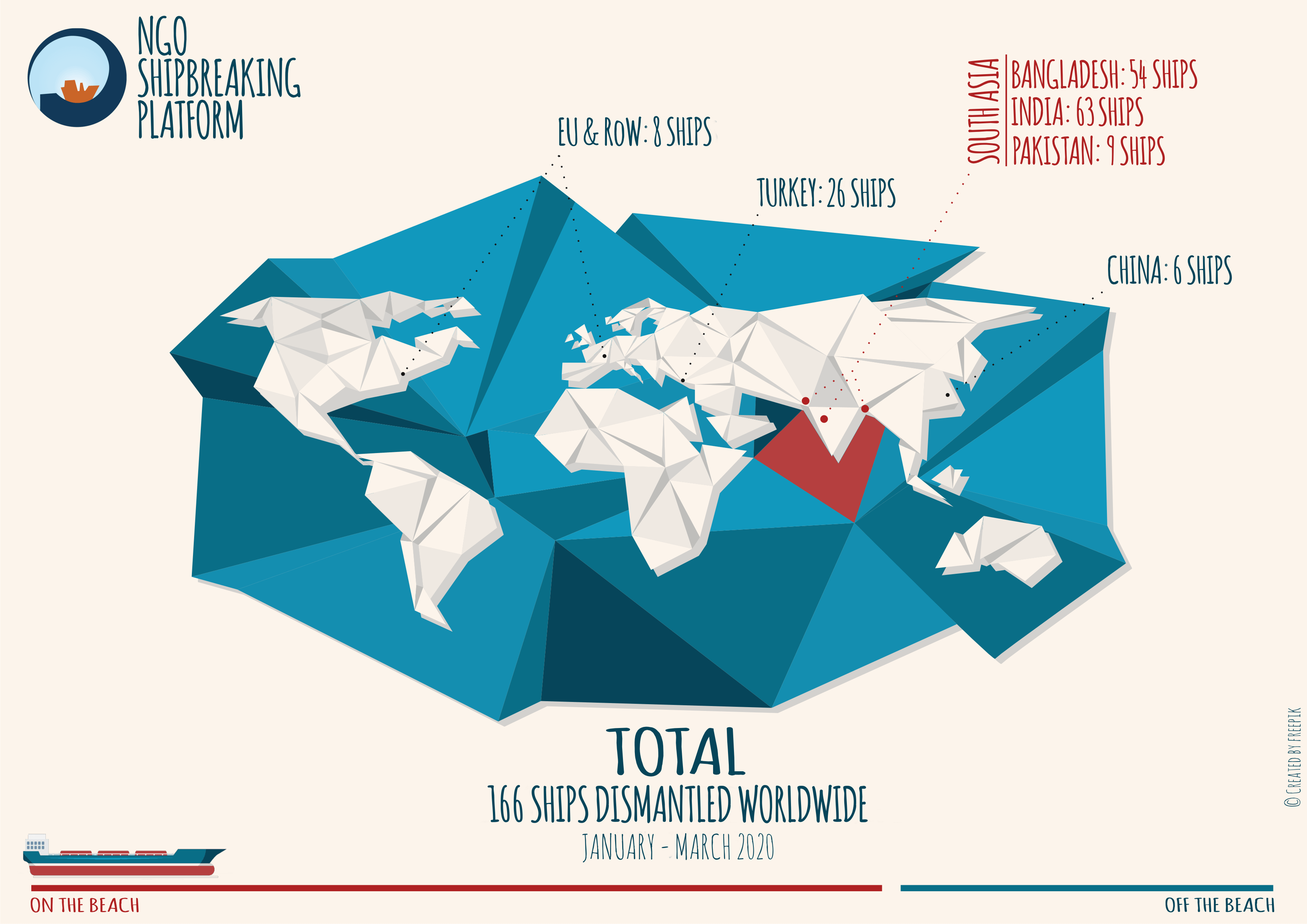
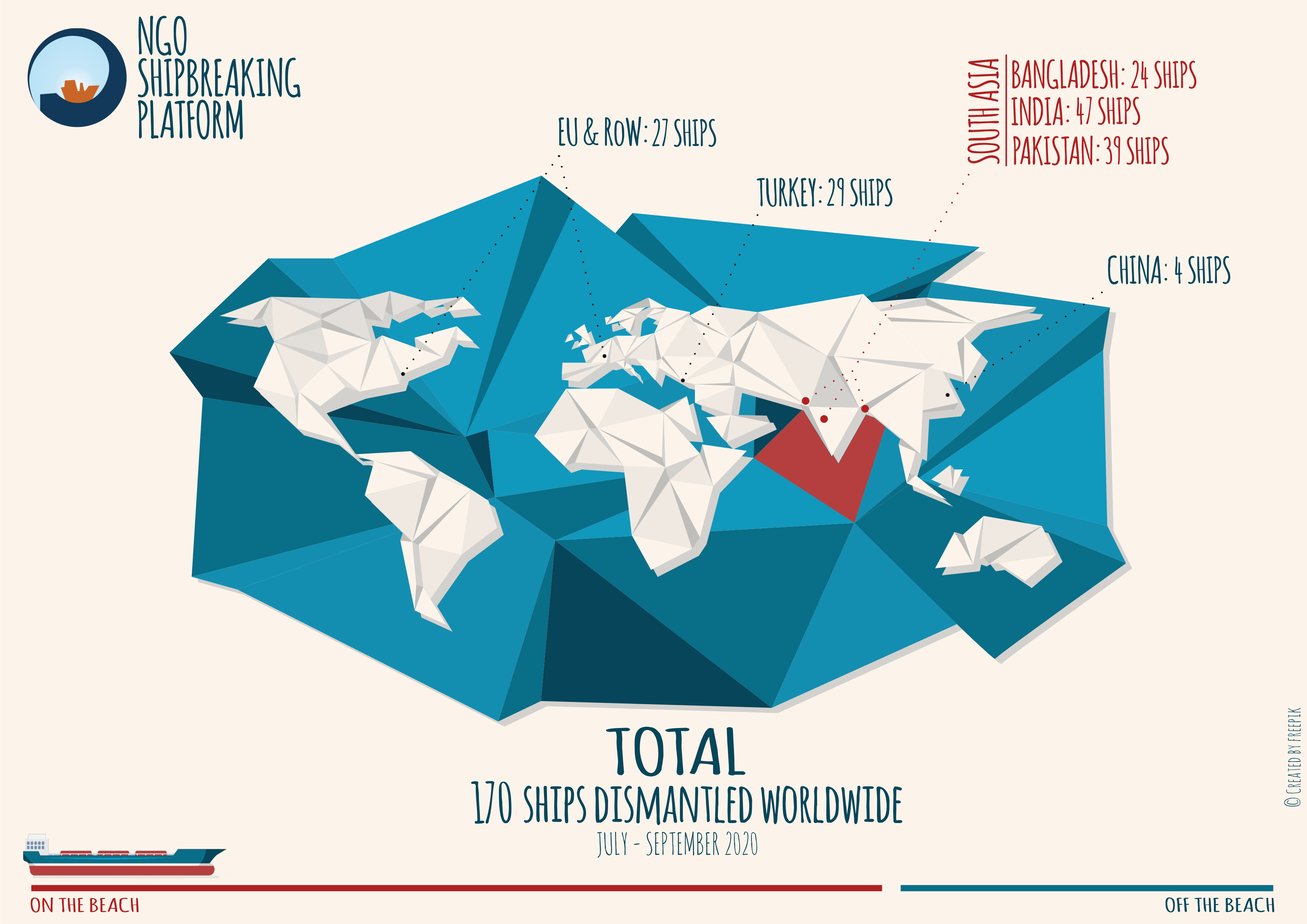
There were a total of 170 ships broken in the third quarter of 2020. Of these, 110 ships were sold to the beaches of South Asia, where, despite several yards being closed due to the Covid-19 pandemic, shipbreaking activities continued to put workers’ lives at risk. Between July and September, at least four workers were severely injured and one worker lost his life in Bangladesh.
On July 1, Rohul (47 years old) suffered an accident at KSB Steels shipbreaking yard. He fell and broke five ribs while dismantling the ship STELLAR IRIS (IMO 9083093), owned by South Korean company Polaris Shipping. On the same day, Mozaffor (42 years old) fell down while dismantling another Polaris’ vessel, the STELLAR JOURNEY (IMO 9050230), at RA Shipbreaking yard. Mozaffor was transferred to Dhaka Hospital as the medical assistance was inadequate in Chattogram.
On July 20, Rashidul Islam (45 years old) died while dismantling an unidentified vessel at N.R. Shipbreaking yard. Rashidul was fatally hit by a falling object.
On July 21, Faruk (24 years old) got injured at Arefin Shipbreaking yard. He was breaking the Japanese-owned vessel INNOVATOR (IMO 8508905) when an iron plate hit his head.
On August 27, Mokbul (40 years old) suffered an accident at T.R. Shipbreakers yard, owned by Didarul Alam, a member of the Bangladeshi Parliament. He was hit by an iron plate in his back. Mokbul did not receive any treatment or compensation from the yard owner in order to satisfy his livelihood needs.
In the third quarter of 2020, Greek ship owners sold the most ships to South Asian yards, closely followed by Japanese, Russian and South Korean owners. South Korean company Polaris Shipping sold another two vessels to Pakistan. The ship owner, which hit the headlines in June for the scuttling of the ore carrier STELLAR BANNER off the coast of Brazil, has sold a total of seven ships for dirty and dangerous breaking in Bangladesh and Pakistan this year.
In April, we urged Bangladesh, India and Pakistan to halt the import of a highly toxic offshore unit that had illegally departed from Indonesia. The Floating Storage and Offloading (FSO) tanker J. NAT (now renamed RADIANT) left Indonesian waters despite local activists having warned Indonesian authorities about the toxicity of the vessel. Following our actions and local media reports, the government of Bangladesh directed all departments concerned not to allow the ship to enter Bangladeshi territory. Similarly, Indian authorities have recently warned Alang shipbreaking yards not to accept the toxic tanker for scrapping. Maritime sources now indicate that the vessel is sailing towards Gadani, Pakistan.
Almost one third of the ships sold to South Asia this quarter changed flag to the registries of Comoros, Gabon, Palau and St. Kitts and Nevis just weeks before hitting the beach. These flags are not typically used during the operational life of ships and offer ‘last voyage registration’ discounts. They are particularly popular with the middlemen scrap-dealers that purchase vessels cash from ship owners, and are grey- and black-listed due to their poor implementation of international maritime law.
The high number of flag changes at end-of-life seriously compromises the effectiveness of legislation based on flag state jurisdiction only, such as the European Union (EU) Ship Recycling Regulation. The Platform recorded at least seven ships that de-registered from a European flag registry (e.g. Cyprus, Germany, Malta) prior the last voyage to South Asia in order to circumvent EU legislation. The export of one of these ships also breached the Basel Convention’s Ban Amendment, which prohibits the export of hazardous waste, including end-of-life vessels, from the OECD, the EU and Liechtenstein to other countries – primarily developing countries or countries with economies in transition. The Ro-Ro cargo ship ZERAN, owned by Polish Ocean Lines, swapped its Maltese flag to that of Panama and illegally left Turkish waters at the end of July. It was beached in Bangladesh in September.
Investigations have been launched by authorities in Iceland following the illegal export of two container vessels owned by Icelandic company Eimskip to India. Icelandic program Kveikur released a documentary on the murky sale of the two ships. Eimskip’s counterpart to the sale was none other than GMS, one of the most well-known cash buyers of end-of-life ships.
Click here or on the image below to access the full version of our quarterly report.