France must act responsibly
The French Courts stopped the scrapping of the asbestos-laden aircraft carrier Clemenceau on the beach of Alang, India [1]. Fifteen years later, France is faced with a second toxic headache. The Clemenceau’s sister ship São Paulo (ex Foch) will soon be dismantled and the French government must approve of the dismantling destination.
The vessel was sold by the French Navy to Brazil in 2000, where it became the new flagship of the Brazilian Navy. After countless serviceability issues, which impeded the ship’s operation for more than three months at a time without the need for costly maintenance, it was formally decommissioned; its auctioning began last year in Rio de Janeiro. So far, both EU-approved ship recycling facilities and yards located on the infamous beach of Alang have submitted documentation to participate in the bidding process.
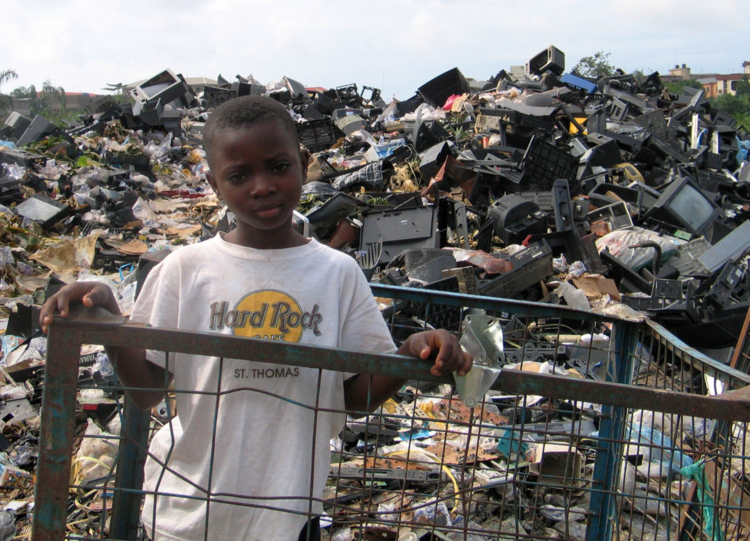
The São Paulo, as the Clemenceau, contains large amounts of hazardous substances within its structure. It is estimated that onboard the vessel there are approximately 900 tons of asbestos and asbestos-containing materials, hundreds of tons of PCB-containing materials and large quantities of heavy metals. The NGO Shipbreaking Platform, BAN, BAN Asbestos France, IBAS and Brazilian ABREA have already alerted both Brazilian and French authorities about the legal, environmental and health risks linked to breaking toxic ships on the beaches of South Asia.

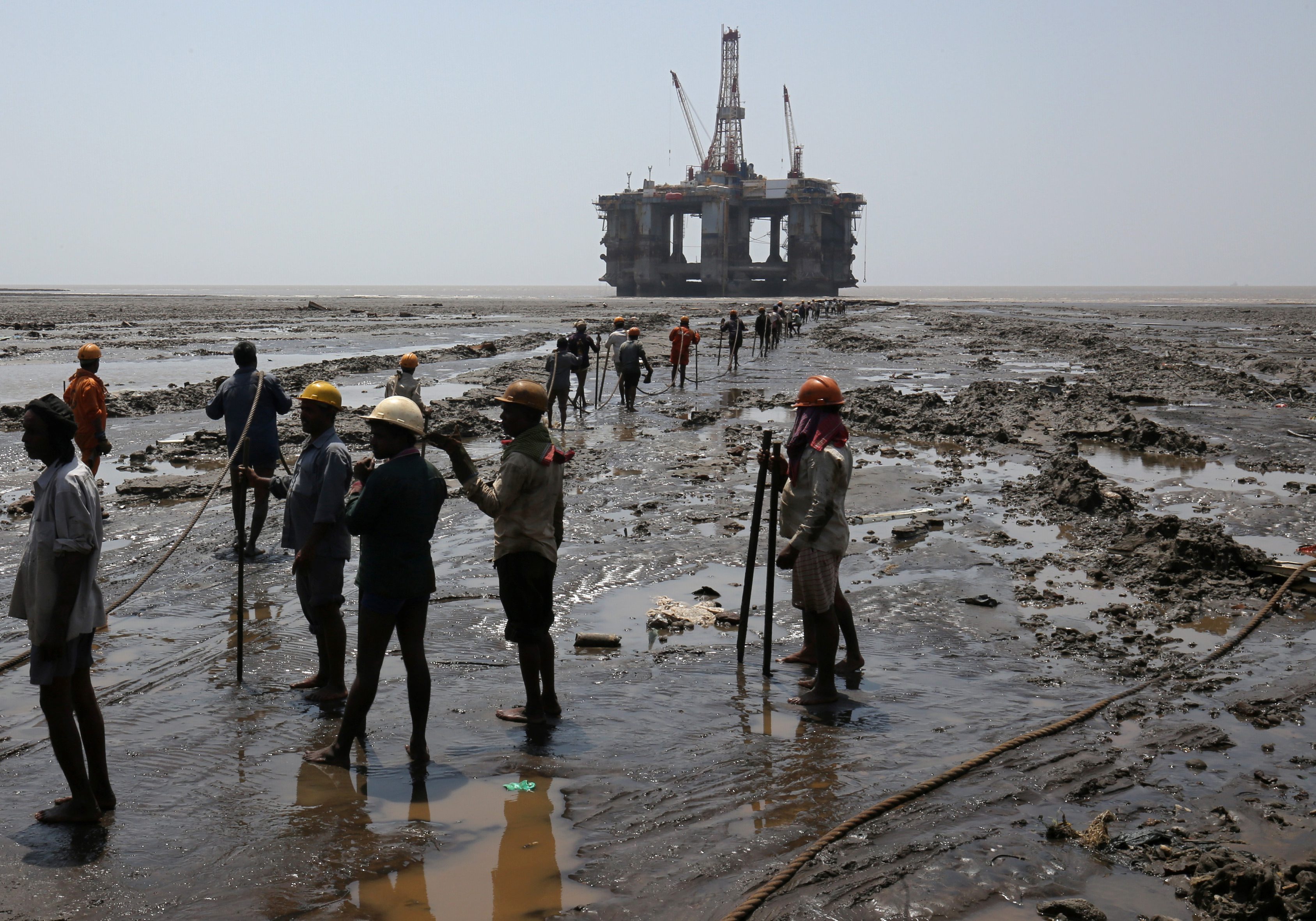
On the ship-breaking beaches of South Asia it is impossible to contain pollutants, including heavy metals and oil residues, as there are no impermeable structures and flooring in the primary cutting zone. The lack of adequate personal protective equipment at the beaching yards, as well as the lack of adequate health facilities, is of grave concern and has been highlighted in recent reports.
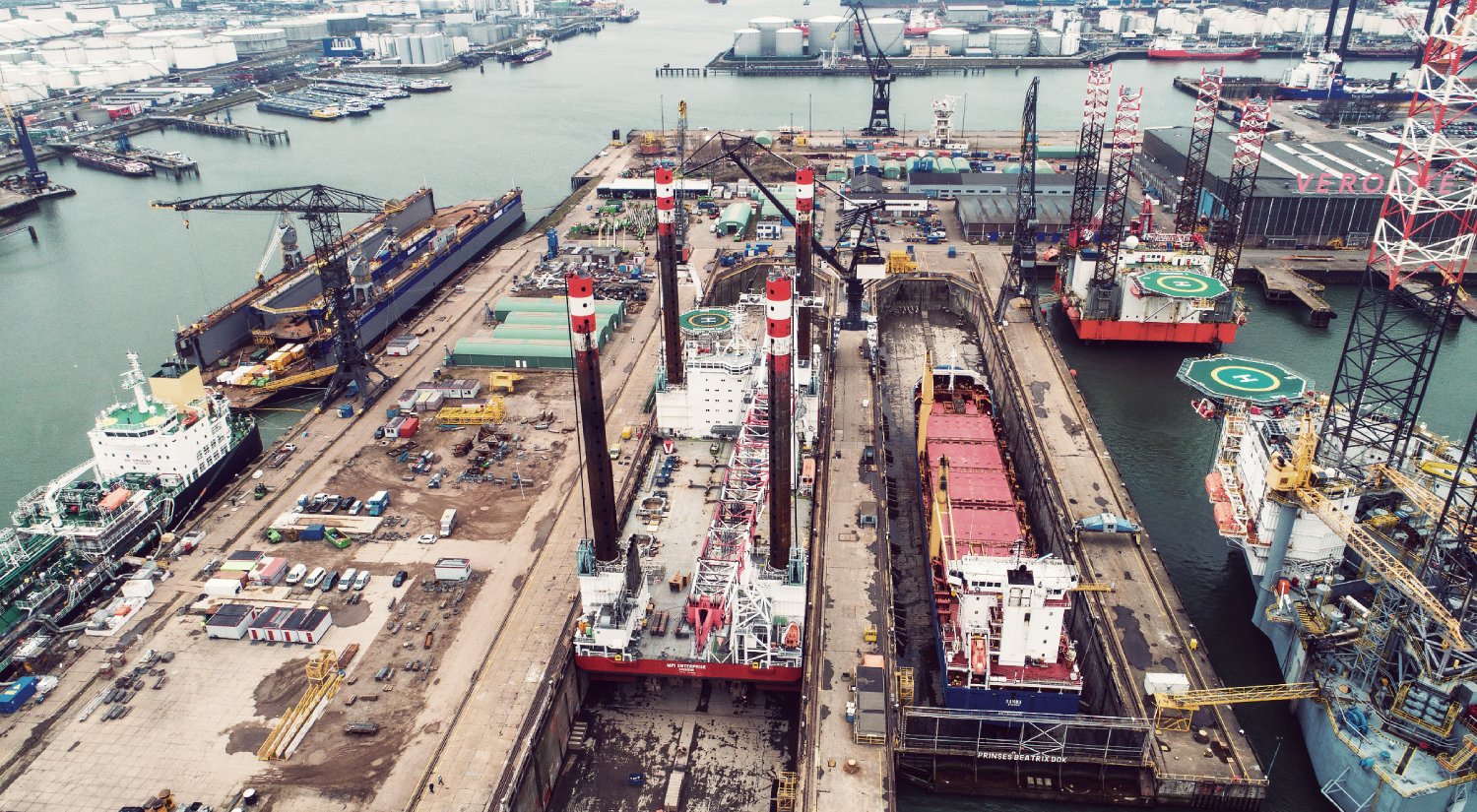
NGOs call upon Brazilian and French authorities to make sure the São Paulo does not end up on a South Asian beach and is safely recycled in an EU-listed yard or converted to other use.
NOTE
[1] On 31 December 2005, the Clemenceau left France despite fierce protests about improper disposal and a lack of facilities for the management of toxic waste on the beaches on South Asia. After having been boarded by activists, held by Egyptian authorities, been blocked from entering Indian waters by the Supreme Court of India, the warship was ordered to return to France by French President Jacques Chirac. It ended up been dismantled in a yard near Hartlepool, UK.