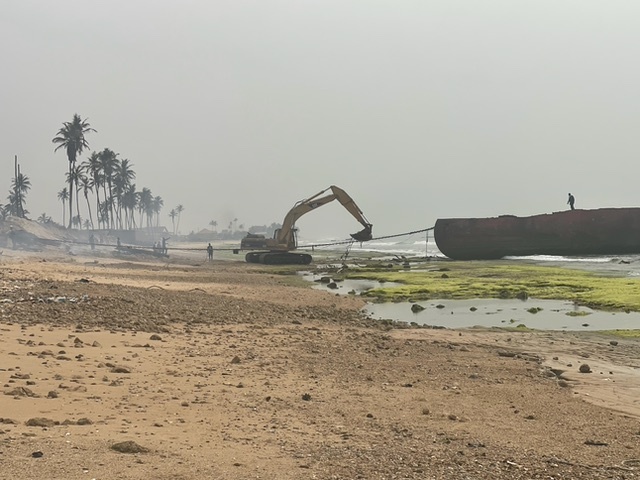
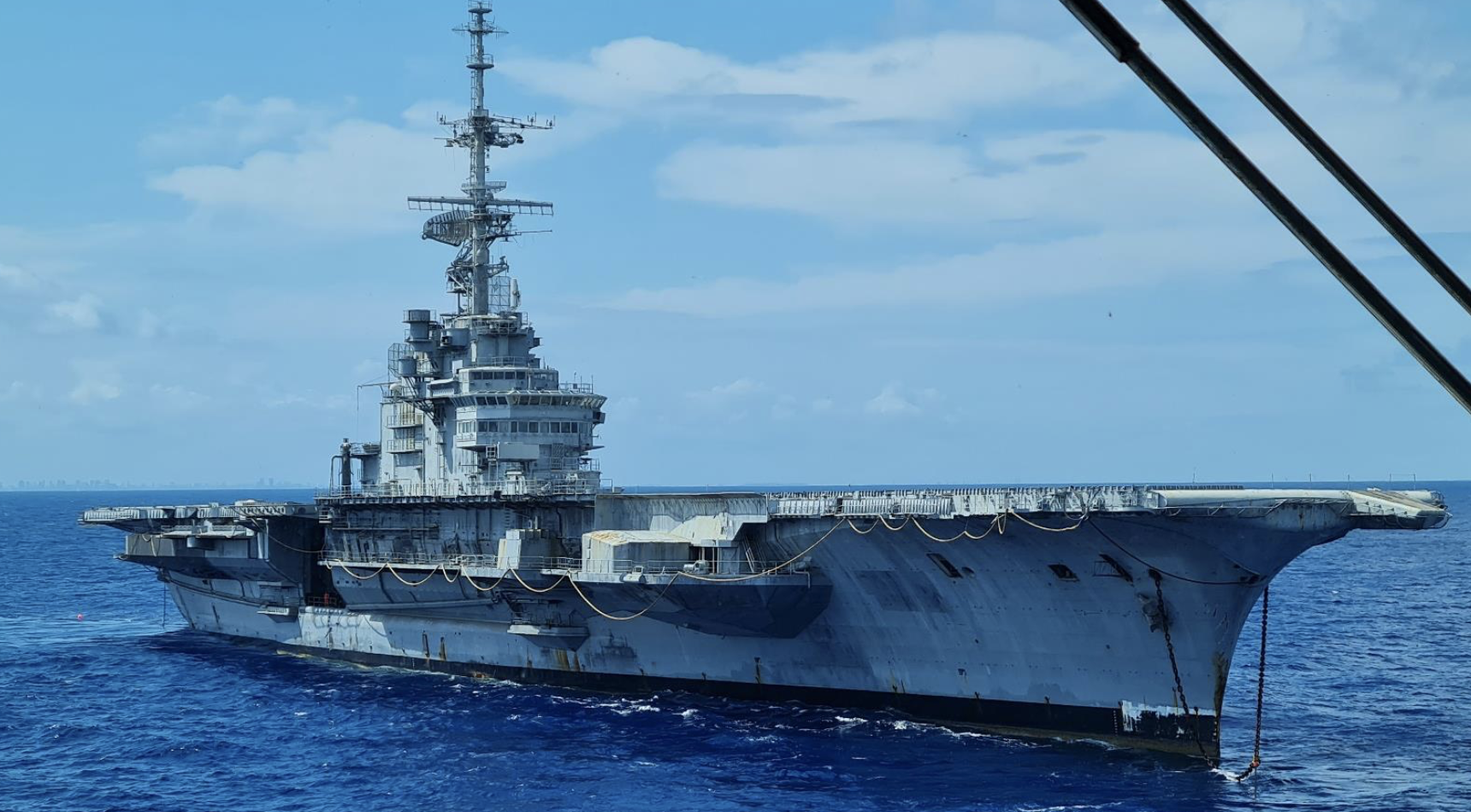
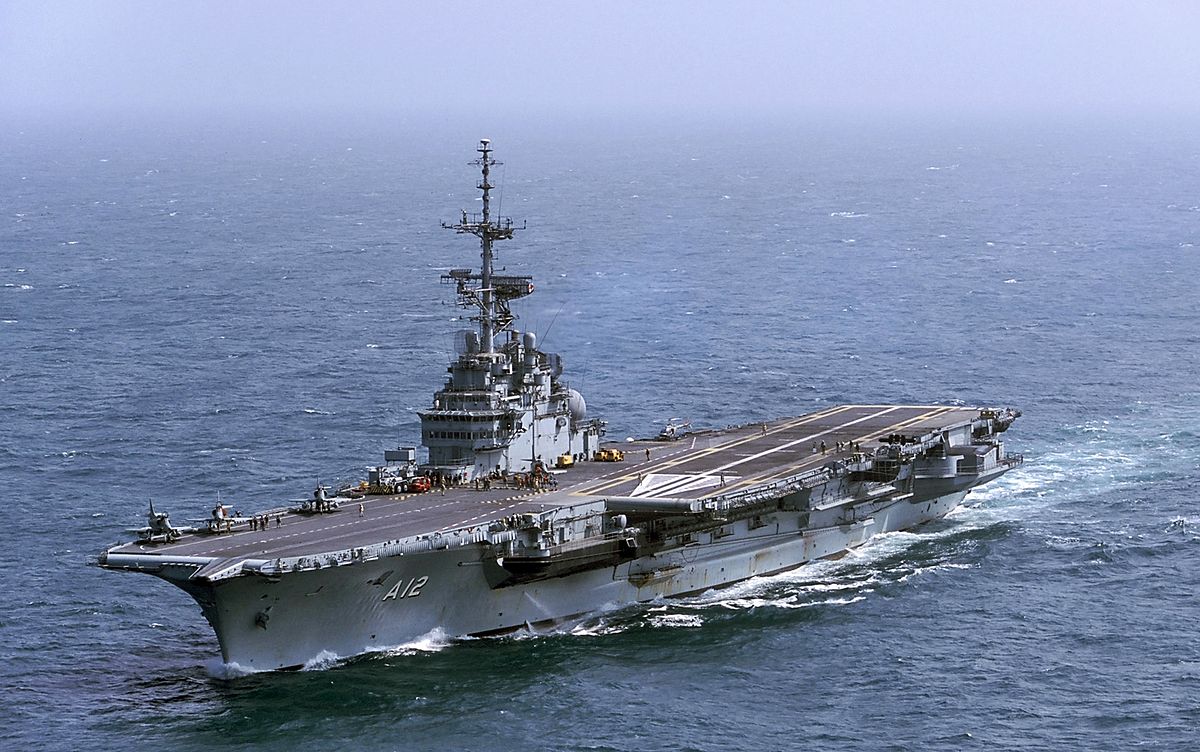
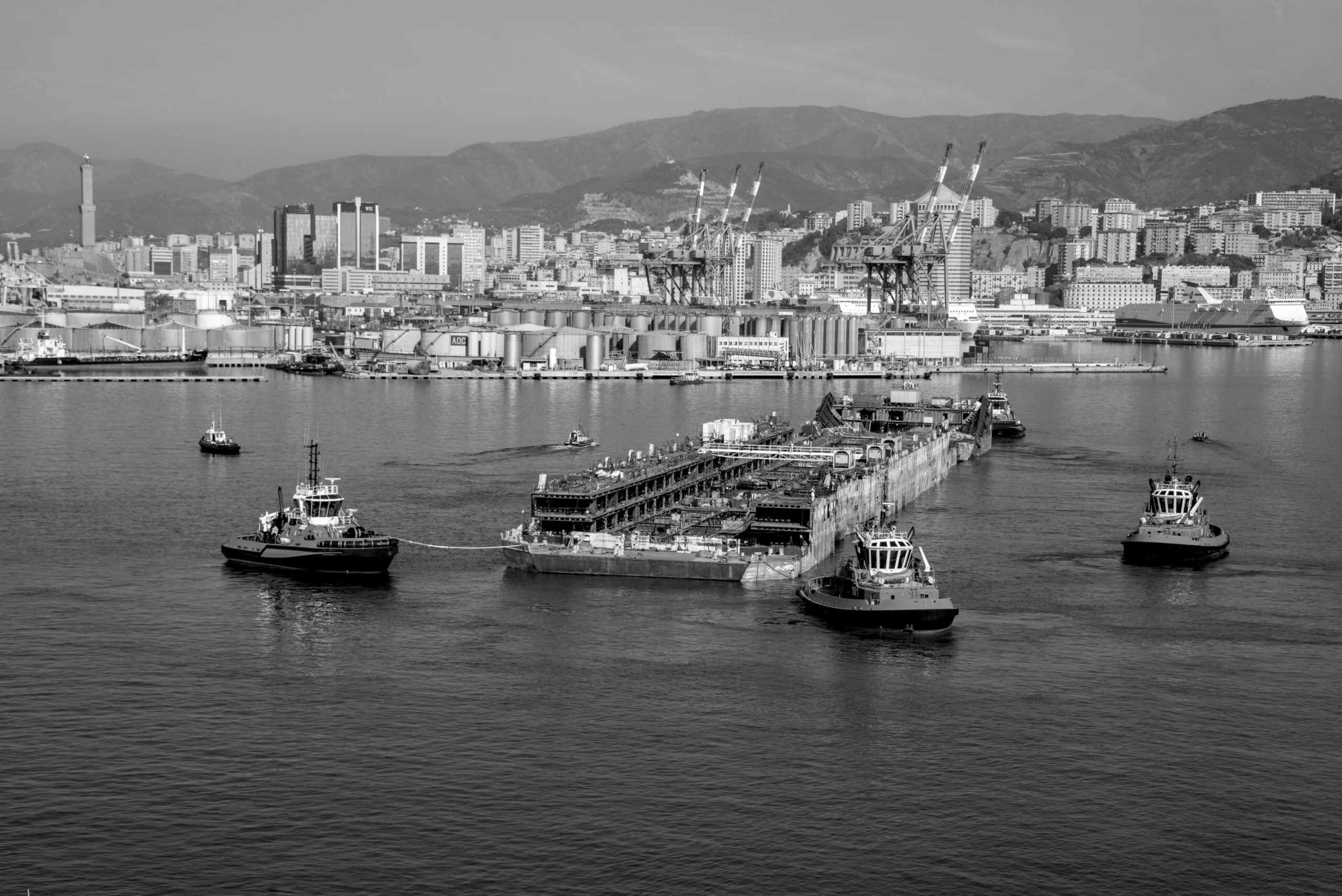
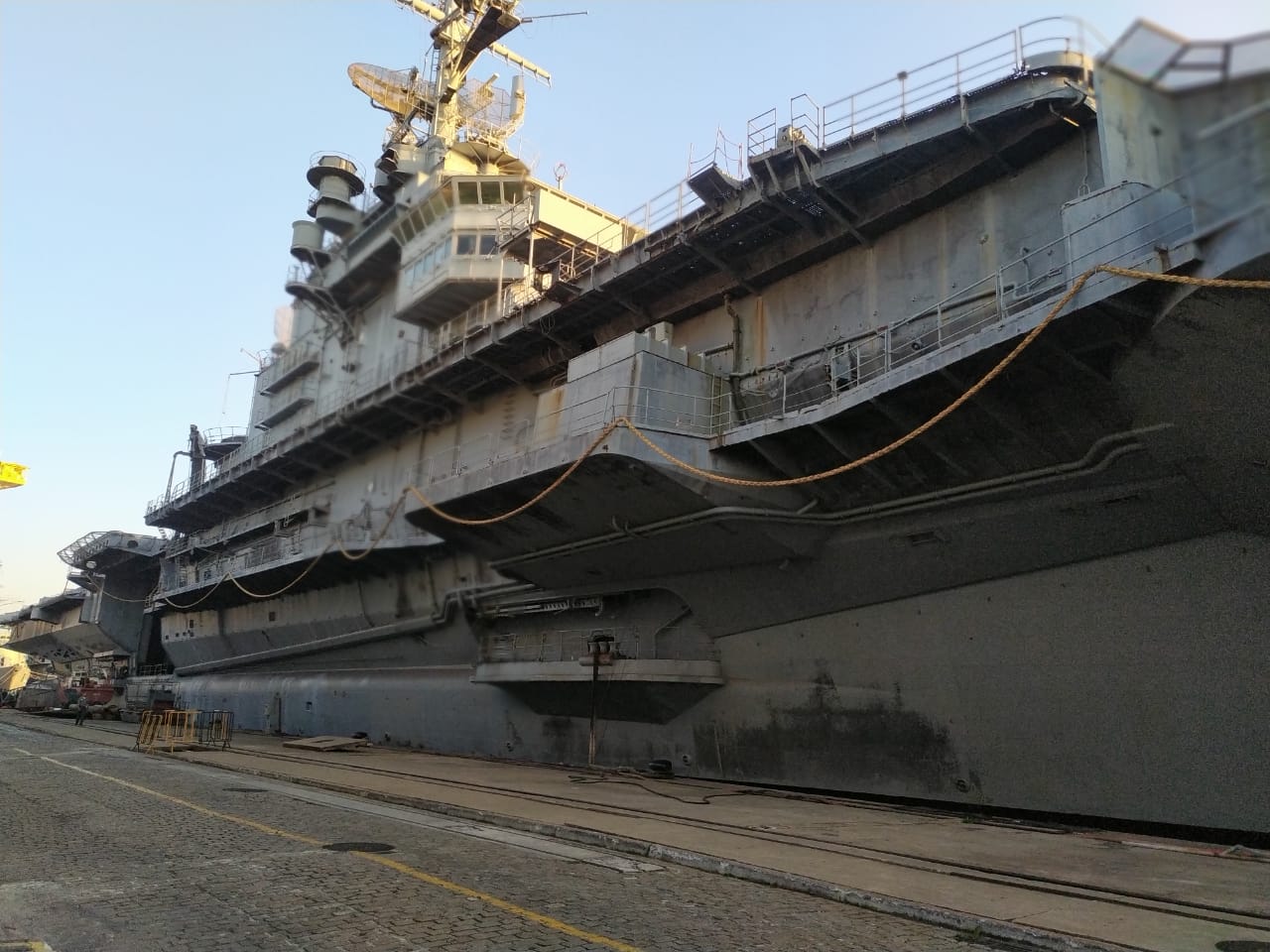
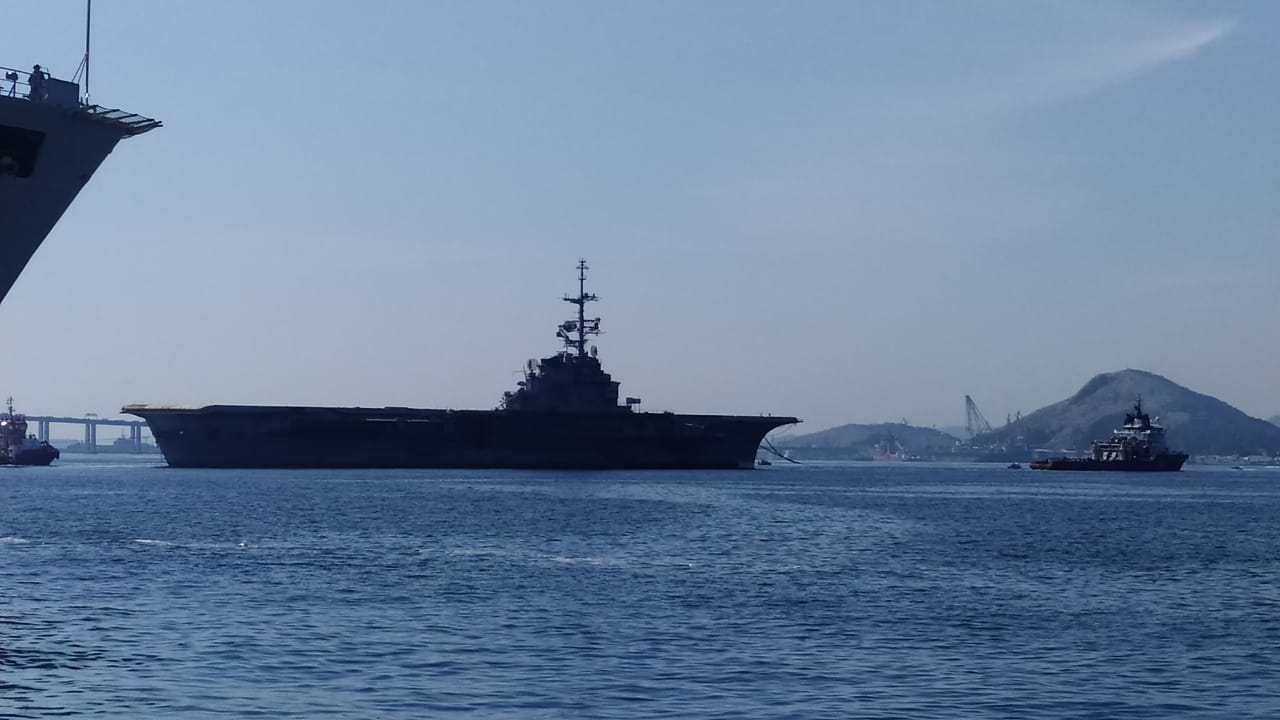
The NGO Shipbreaking Platform, Basel Action Network (BAN), BAN Asbestos France, Henri Pézerat Association (Work, Health, Environment), International Ban Asbestos Secretariat (IBAS), İstanbul Isig Meclisi, Greenpeace Mediterranean and Brazilian ABREA are all calling for the government of Brazil and the owner of the ship (SOK Denizcilik Ve Tic LTD STI ME) to comply immediately with the injunction issued by the 16th Federal Court (Rio de Janeiro) and return the ship to Rio de Janeiro. In an open letter to IBAMA (Brazilian Institute for the Environment and Renewable Natural Resources), the Brazilian government agency responsible for authorizing the export under the Basel Convention, BAN and the NGO Shipbreaking Platform cited likely violations of established law.
Defiance of Brazilian Federal District Court Injunction
On August 4, just a few hours after the departure of the vessel, a judge of the 16th Federal Court issued an "Order to Return the Ex-Nae SÃO PAULO to Rio de Janeiro.” IBAMA, as the entity charged with authorizing the shipment under the Basel Convention, has clear responsibility and authority to recall the export. As no action has been taken by the Brazilian authorities, the non-governmental organisations have consequently alerted INTERPOL to the situation.
Lack of Required Insurance
According to the insurance documents filed by IBAMA prior to the ship's departure, the accident and damage insurance elapsed in May 2022. Yet, insurance required by the Basel Convention must be in place before the export. If the filed documents are correct and the SÃO PAULO was not properly covered by insurance, it is unlikely that any insurance company will correct this failure now and renew the policy, as the ship's export is currently under an injunction and a cloud of illegality and uncertainty.
Export without Notification to, and Consent from, Transit States
According to the towing plan filed by IBAMA, the transboundary movement of the SÃO PAULO from Brazil to Turkey will pass through the Strait of Gibraltar and thus will move through the territorial waters of Spain, the UK, and/or Morocco. Under the Basel Convention, all transit states must be notified and give their consent before the export can commence. However, in the correspondence between the NGOs and IBAMA, it was incorrectly asserted by IBAMA that the prior notification to transit states was not needed if the ship did not stop in a port. The Basel Convention's definitions clarify that transit includes passage through territorial waters. Thus, depending on the precise route chosen, Spain, Morocco, the UK, Malta, Italy, and Tunisia should have been notified and their consent should have been received prior to departure. Failure to do this makes this export illegal traffic under the Convention. Without such notification, Spain, Morocco and UK should deny passage.
Export to Parties that have Prohibited the Import of Hazardous Waste
When Parties notify the Basel Secretariat that they possess an import prohibition of hazardous wastes, all Parties must respect that prohibition under the Convention. Turkey has notified not only that they have a national import ban on hazardous wastes, but they are also Party to the Izmir Protocol of the Barcelona Convention, which requires Turkey to ban imports of hazardous wastes. In the case of the SÃO PAULO, Brazil, as an exporting state Party must prohibit all exports to Turkey. Yet Brazil allowed this export.
Toxic Waste Quantification Discrepancies
A complete and accurate assessment of the hazardous materials (waste) contained within the ship structures is a requirement prior to export under the Basel Convention. However, it appears that the Inventory of Hazardous Materials (IHM) prepared for the SÃO PAULO by Grieg Green may have greatly underestimated the quantities of cancer-causing asbestos, toxic paints, radioactive substances, and Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs). In 2006, Greenpeace International commissioned Mr. Aage Bjorn Andersen, an expert in the field of hazardous material surveys on marine vessels, to assess the sister ship CLEMENCEAU. His estimate was 760 metric tons of asbestos. In contrast, the recent IHM estimated just 9.6 tons. And, in a subsequent letter, Grieg Green admitted that figure could be significantly off the true amount. Similarly, the CLEMENCEAU was estimated to contain 165 tons of PCB material (levels higher than 50/ppm concentrations). The IHM for the SAO PAULO found no PCBs in the small number of samples taken and estimated no PCBs. For a ship built in 1957 when use of PCBs was ubiquitous, this finding of no PCBs is doubtful. Without a proper assessment of hazardous materials, the proper capacity to manage the waste cannot be determined.
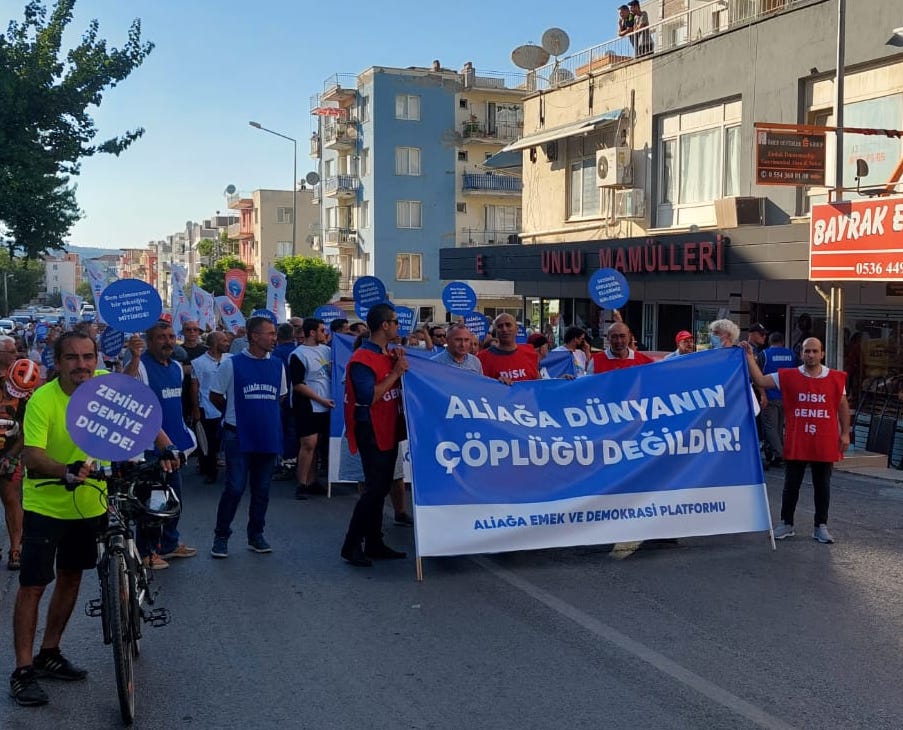
Meanwhile, communities in Turkey are alarmed about the incoming hazardous wastes that will potentially harm workers and need to be managed and disposed of safely. They have organized daily vigils to take place in Aliaga.