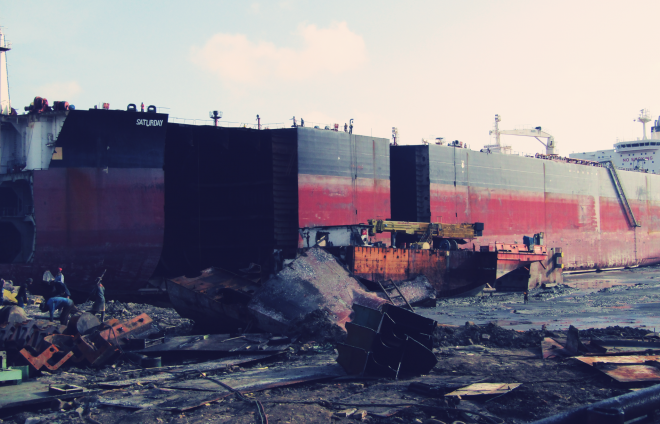
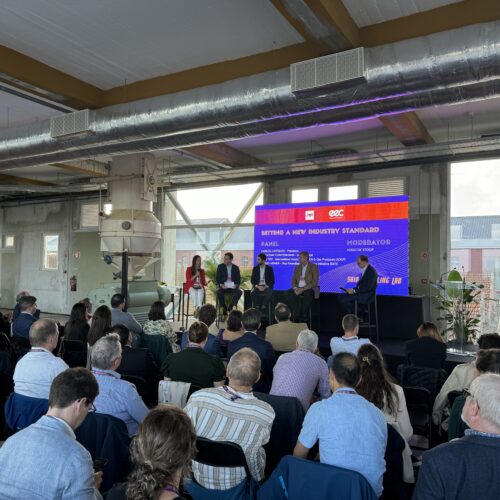
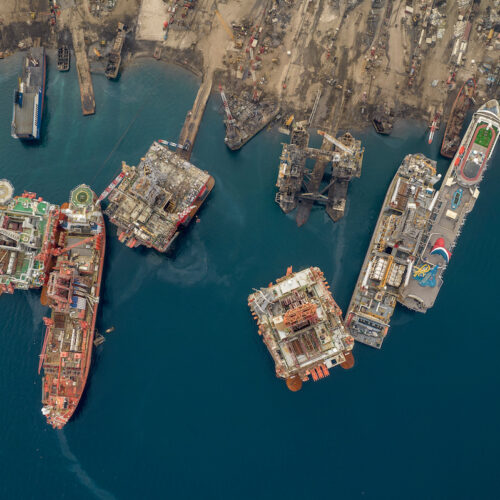
Over 100 participants from across the globe, including recyclers, ship owners, policymakers, researchers, and environmental advocates, met in Lisbon on 9-10 October for the NGO Shipbreaking Platform’s second edition of the Ship Recycling Lab. With a sharp focus on environmental responsibility and cutting-edge technologies, the event showcased companies that already are sustainably recycling vessels, as well as ongoing research and policy commitments aimed at further scaling and improving practices.
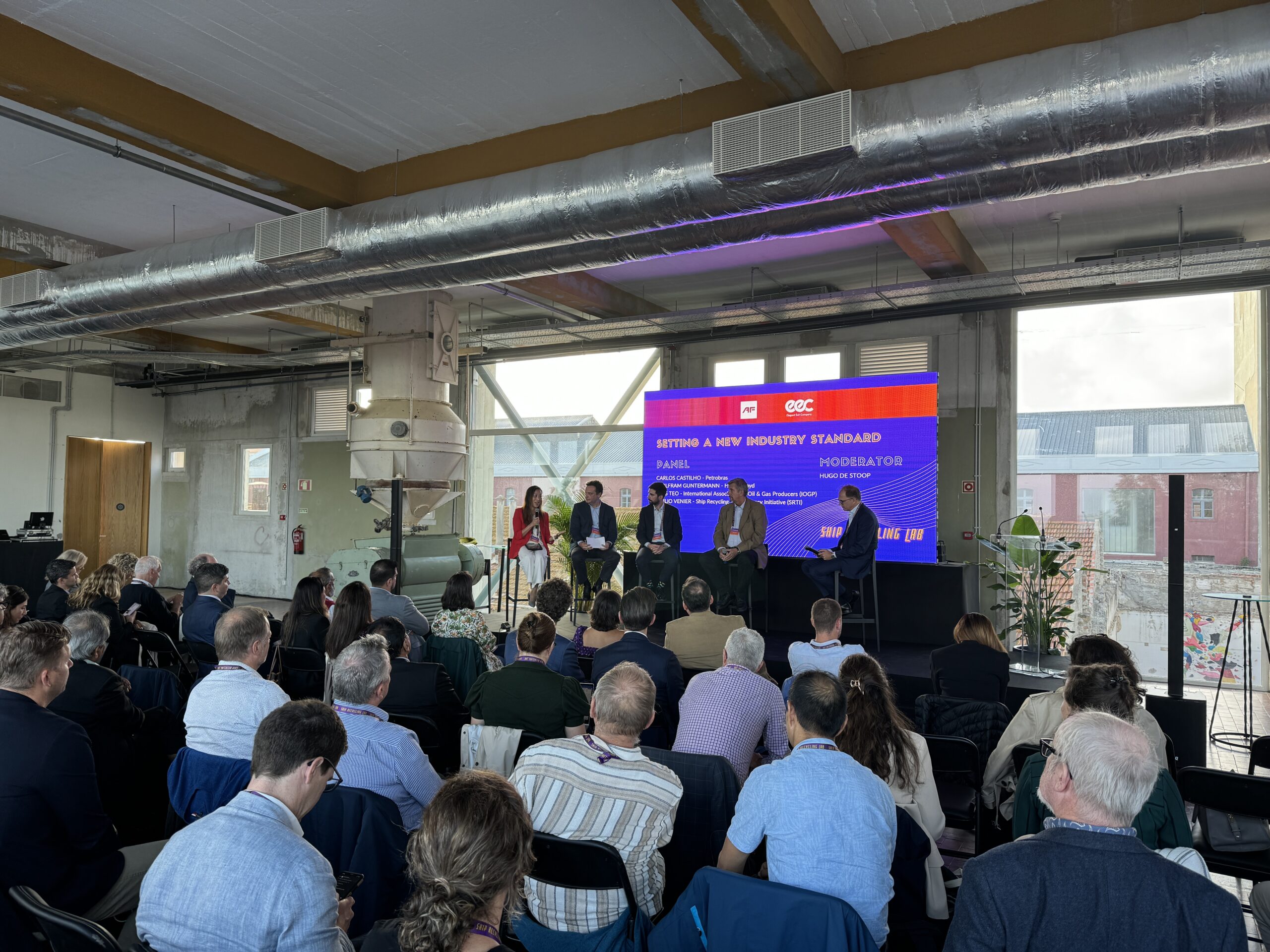
From Brazil to the Middle East, new strategies are pushing for safe and clean ship recycling. Elegant Exit Company shared experiences recycling their first ship in a dry-dock in Bahrain, while Petrobras introduced its new "off the beach" policy and pilot projects designed to boost Brazil’s domestic capacity. In Europe - and on home-turf at the Lab - Lisnave shared that they intend to add recycling to their repair and maintenance activities at their Setubal yard.
Participants at the Lab expressed keen interest to look at what the sector can offer in terms of meeting circular economy and climate objectives. Possibilities for a thriving ship recycling hub in Northern Germany driven by a demand for scrap steel were explored, and going forward, EuRIC, the European Recycling Industries' Confederation, announced at the Lab the establishment of a new working group. They will undoubtedly play an important role in raising the issue at the European level and have already identified the need to embed stricter safety and environmental benchmarks into the upcoming revision of the EU Ship Recycling Regulation to ensure a fair level playing field.




The Lab also spotlighted the latest technological advancements, including plasma and water cutting technologies as alternatives to gas cutting, and RFID tracking and blockchain as tools for improving the management of Inventories of Hazardous Materials. AF Offshore Decom captured the attention with their groundbreaking work on upcycling decommissioned assets by generating certified second-hand steel with 95% lower CO2 emissions for the construction sector. Several projects, including SHEREC, Circles of Life, ReCab, and ShipRec, shared ongoing R&D looking at novelties in circular economy principles, including material passports, and AI integration.
Unveiling their new guideline on FSO and FPSO decommissioning, the International Association of Oil & Gas Producers (IOGP) was another stakeholder at the Lab setting a new benchmark for industrial sustainability. Their guideline bans the use of substandard scrapping methods, including beaching, and prohibits dealings with cash buyers — a practice long criticised for fuelling unsafe and unregulated shipbreaking.
Addressing how to foster industrial practices that do not compromise on protecting fragile coastal ecosystems and ocean health, the International Finance Corporation (IFC), part of the World Bank, provided insights on how blue bonds could potentially unlock finance, marking a clear step towards integrating ship recycling into global sustainable finance frameworks. Increased traceability on scrap steel, quality and supply chain were furthermore identified as key to add value and also assist the steel sector in its transition towards meeting industrial decarbonisation targets.