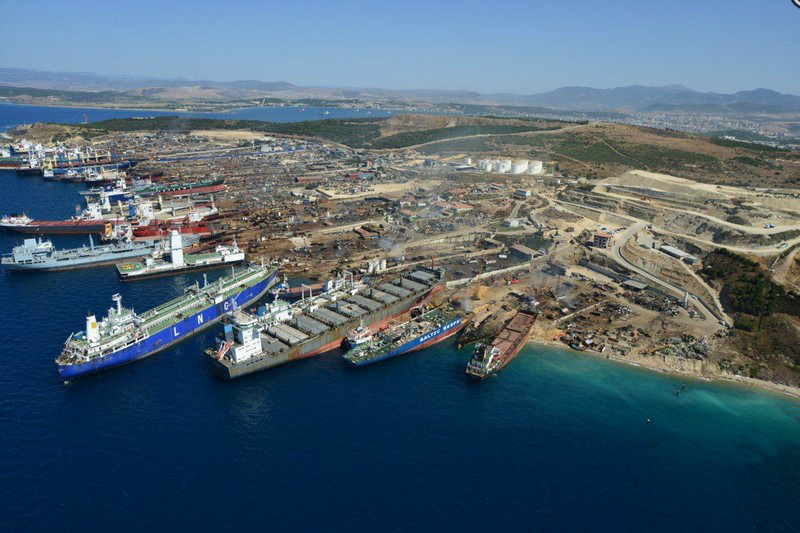
On February 3, the NGO Shipbreaking Platform presented its latest report, Ship Recycling in Turkey – Challenges and Future Directions, in Izmir, Turkey. Attending the event, representatives from local NGOs, unions and concerned citizens engaged in a constructive dialogue on the future outlook of the sector and how to ensure safe and environmentally sound practices.
While the report sheds light on the the diverse challenges faced by the ship recycling sector in Aliağa, it also emphasises the vast potential for fostering sustainable practices in Turkey and outlines a clear path towards achieving this goal. The event in Izmir explored avenues for collaborative efforts aimed at ensuring a robust Environmental Impact Assessment for the sector, the development of appropriate industrial platforms to contain pollutants, and the adoption of cutting-edge technologies to minimize exposure to risks.
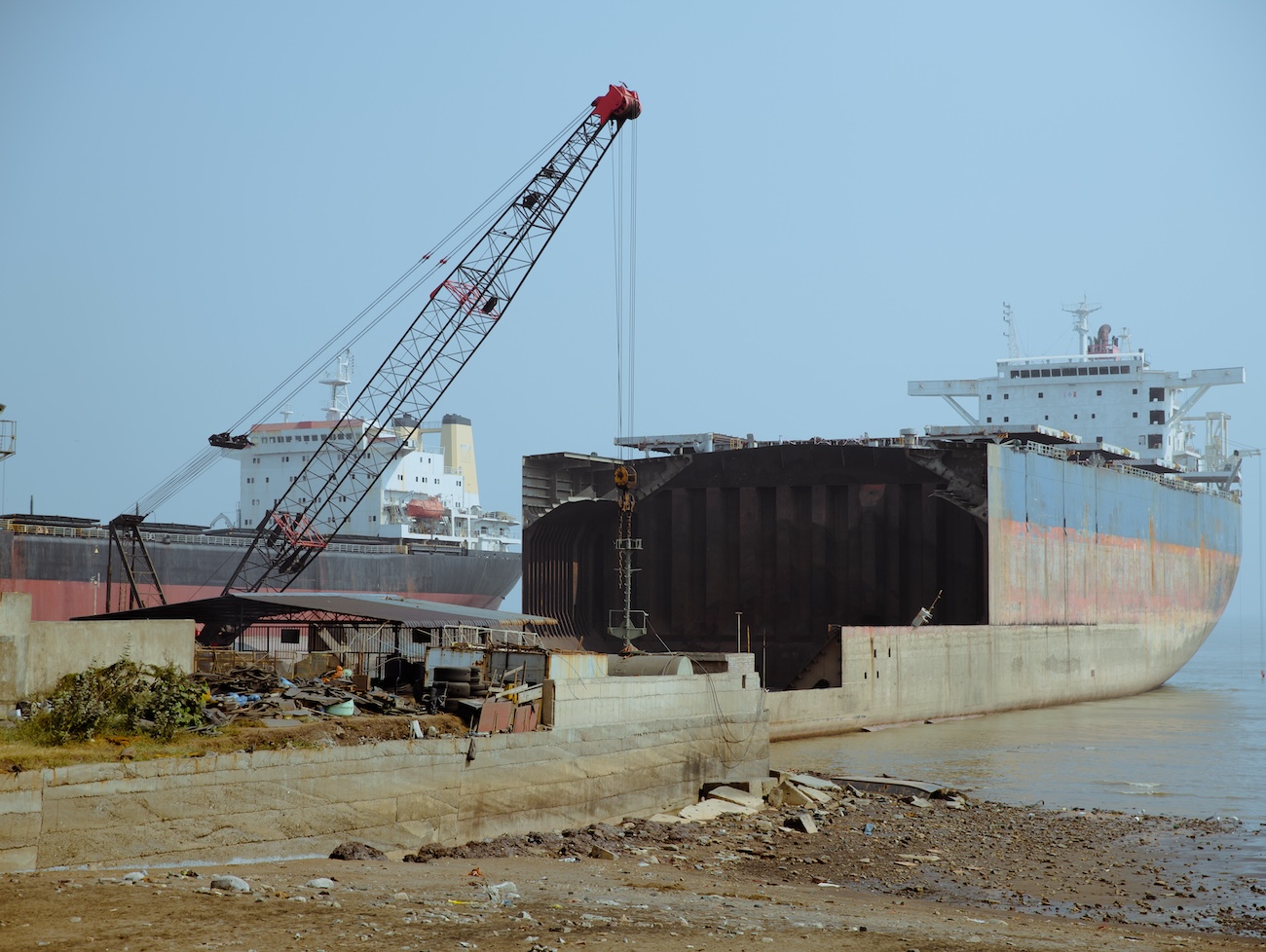
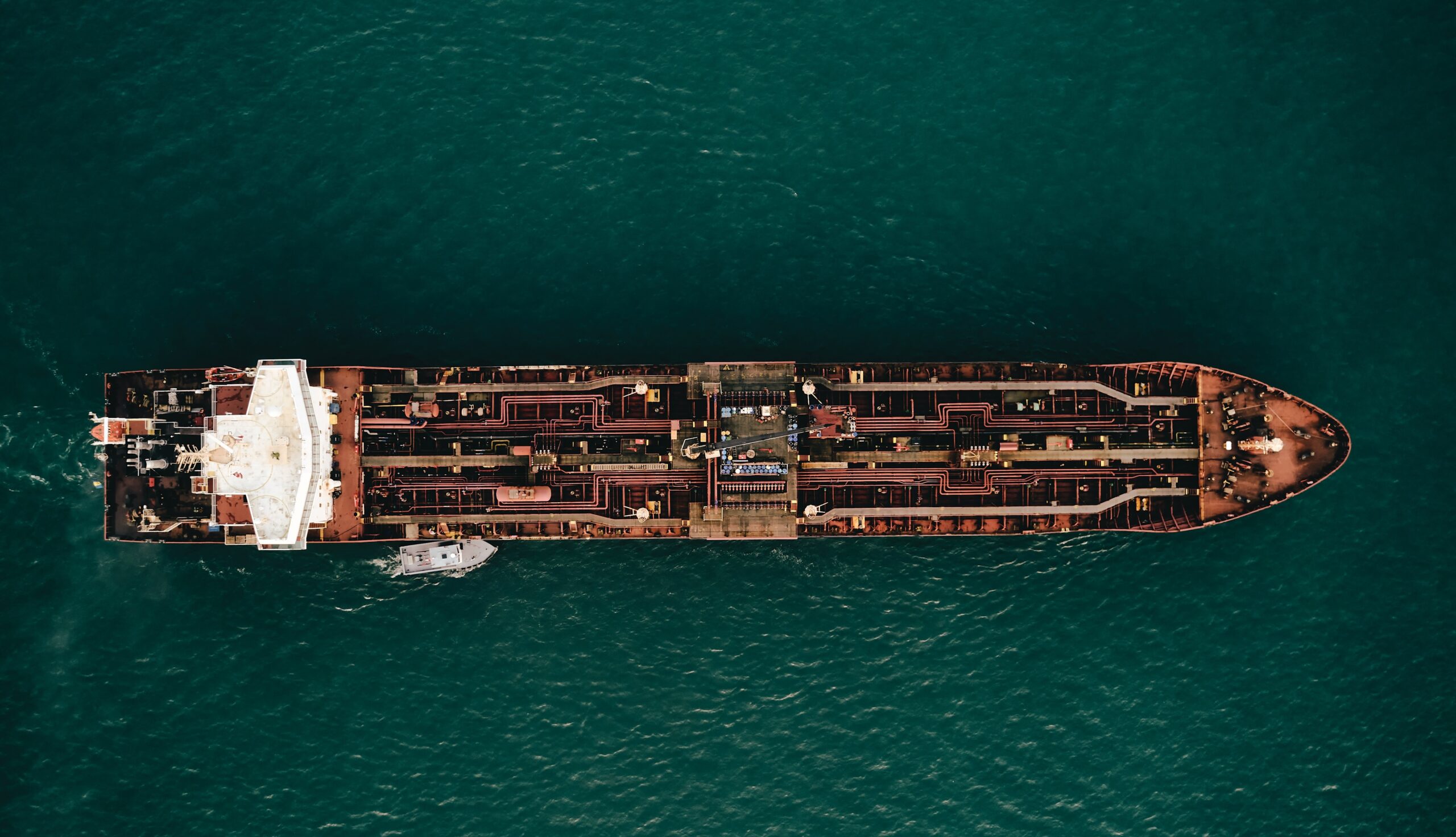
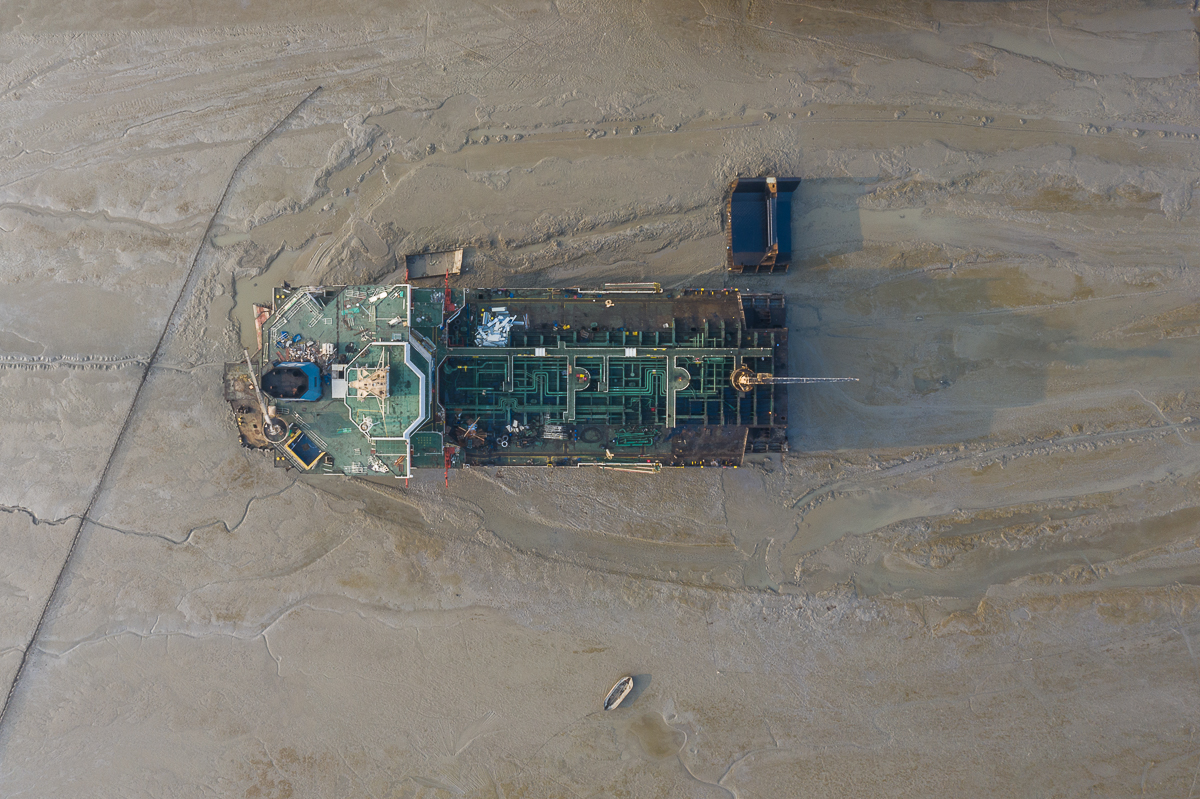
To gain further insights into the initiatives that can drive progress in the Turkish sector, the Platform recommends the reading of the publication by the Ministry of Environment, Urbanism, and Climate, which evaluates the use of new technologies in Aliağa and the move of operations to either floating- or dry-docks.