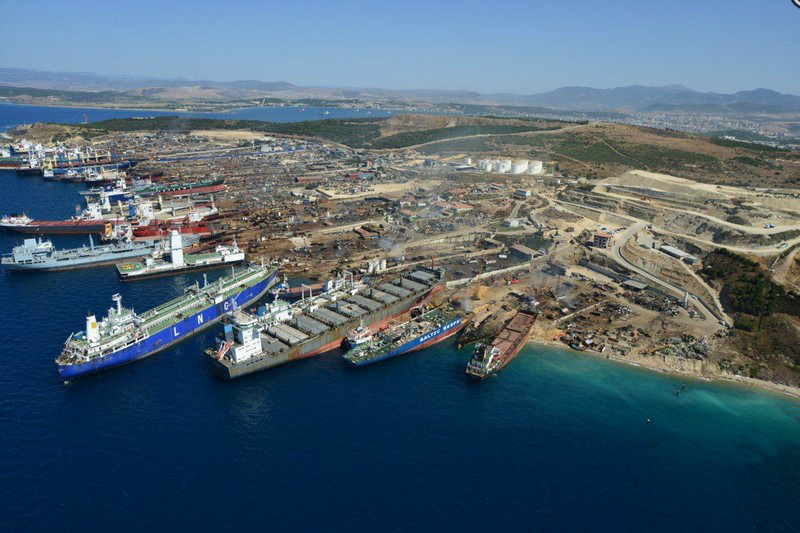
In the last six days, almost the totality of the ship recycling workforce at İzmir Aliağa district, Turkey, has been striking for better employment conditions. Around 1500 workers are claiming that they do not earn enough money, with their recent pay raise remaining below the galloping inflation rate. The action was initiated spontaneously by employees of several ship recycling facilities operating in Aliağa, including some of those recently approved by the EU. Exercising their right of peaceful assembly according to Turkish constitutional provisions, people gathered in front of the offices of the Ship Recycler's Association and, shouting slogans, marched to the yards. The production at all 22 facilities has been halted.
Besides asking for better living wages, workers are also demanding to their employers to provide them with personal protective equipment, and to increase investments in occupational health and safety in the sector. Recently, multiple accidents have been reported. Regrettably, the causes of injuries and deaths in Aliağa have remained the same over the last 30 years. Local NGOs documented at least 44 occupational deaths since 1992. Last year alone, five workers lost their lives, also at EU approved yards. This year, two workers were seriously injured and are currently being treated at the hospital. Whilst Kasım Han was hit by a falling piece on his chest, Osman Gökduman fell from a crane.
Asli Odman, academic at Istanbul Health and Safety Labour Watch, explains that workers are also falling sick and dying of occupational diseases many years after being exposed to toxics found on ships, but these numbers go totally unreported. Cancer rates in Aliağa are much higher than the Turkish average. In fact, asbestos is one of the most common and most hazardous materials found onboard old ships. When extracted, it can break into fine fibres, which can remain in the air for long periods of time. If inhaled, the fibres can lead to fatal diseases such as lung cancer, mesothelioma and asbestosis, the symptoms of which are not apparent for many years. Asbestos fibres, attached to clothing and textiles, can also easily travel to the workers' accommodations, lengthening exposure to the pollutant and putting others living in the same locations at risk. Unsafe working conditions, including the lack of measures taken to manage asbestos properly, have been recently exposed.