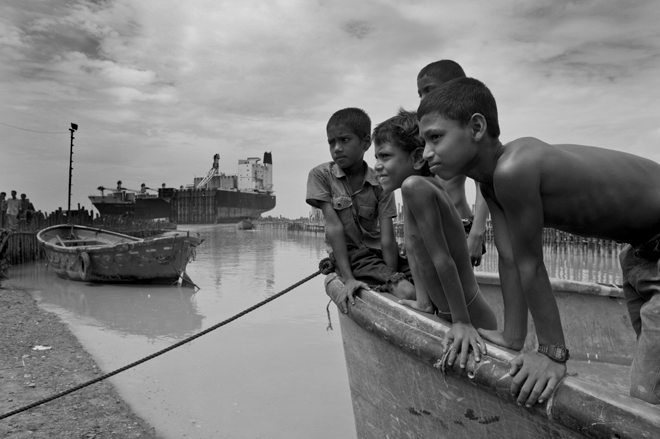
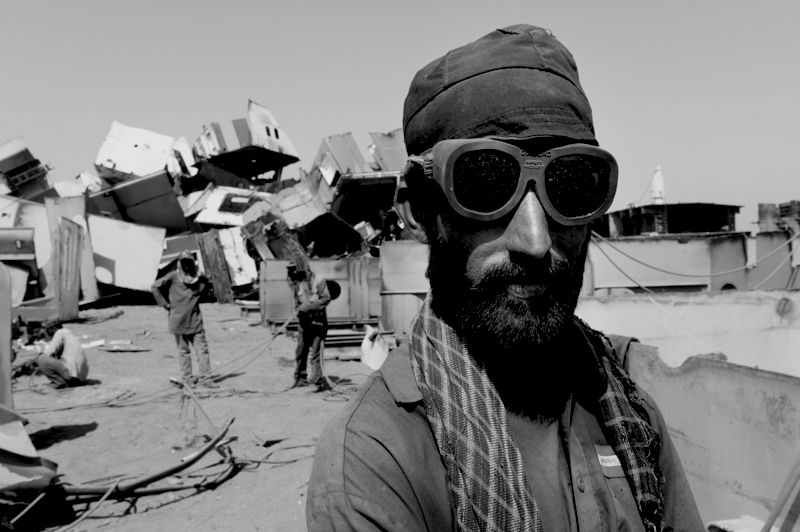
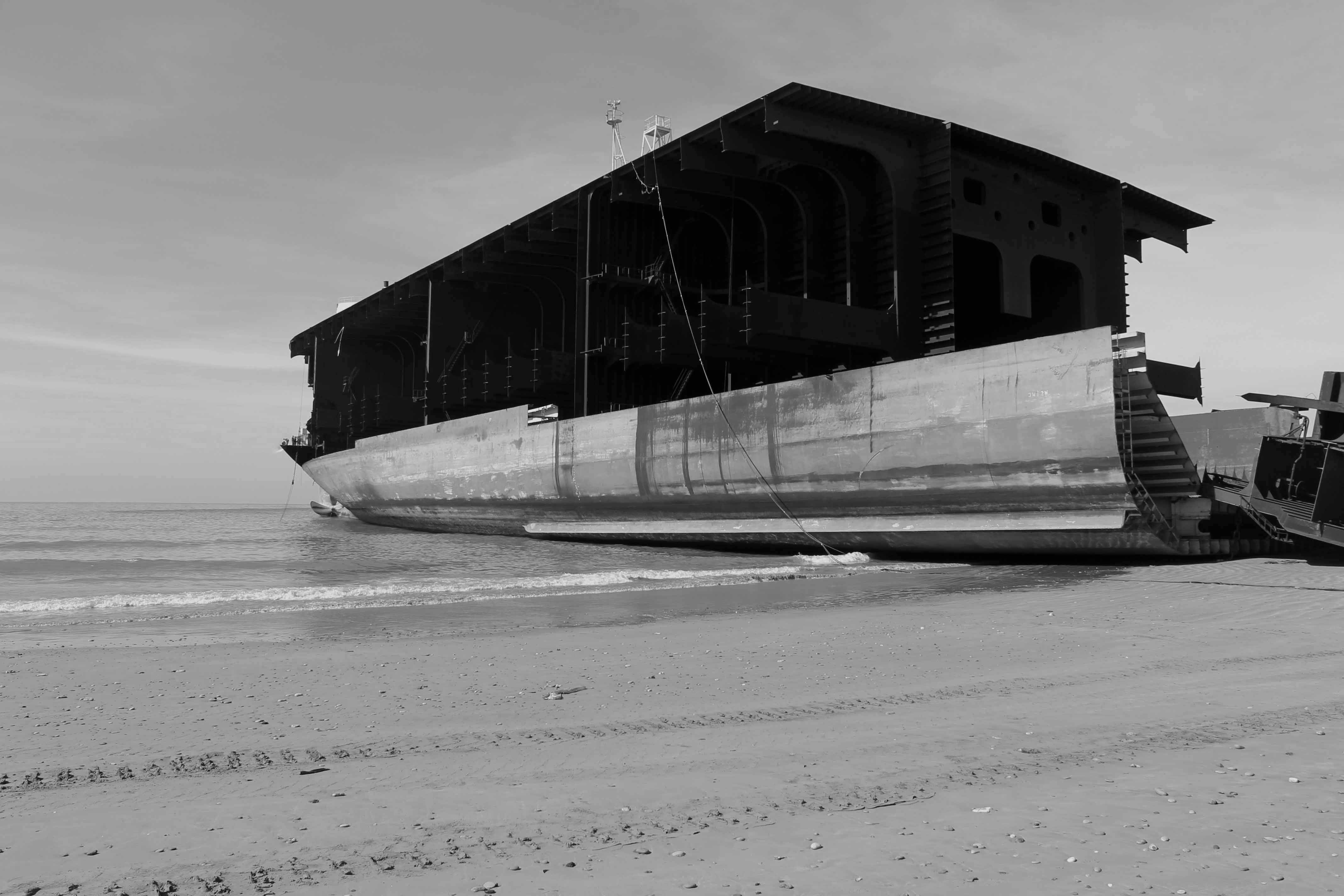
The negative consequences of shipbreaking are real and felt by many. On the one hand, workers – often exploited migrants and some of them children – lose their life, suffer from injuries caused by fires, falling steel plates and the general unsafe working conditions, as well as from occupational diseases due to exposure to toxic fumes and materials. On the other hand, coastal ecosystems, and the local communities depending on them, are devastated by toxic spills and various pollutants leaking into the environment as a result of breaking vessels on beaches.
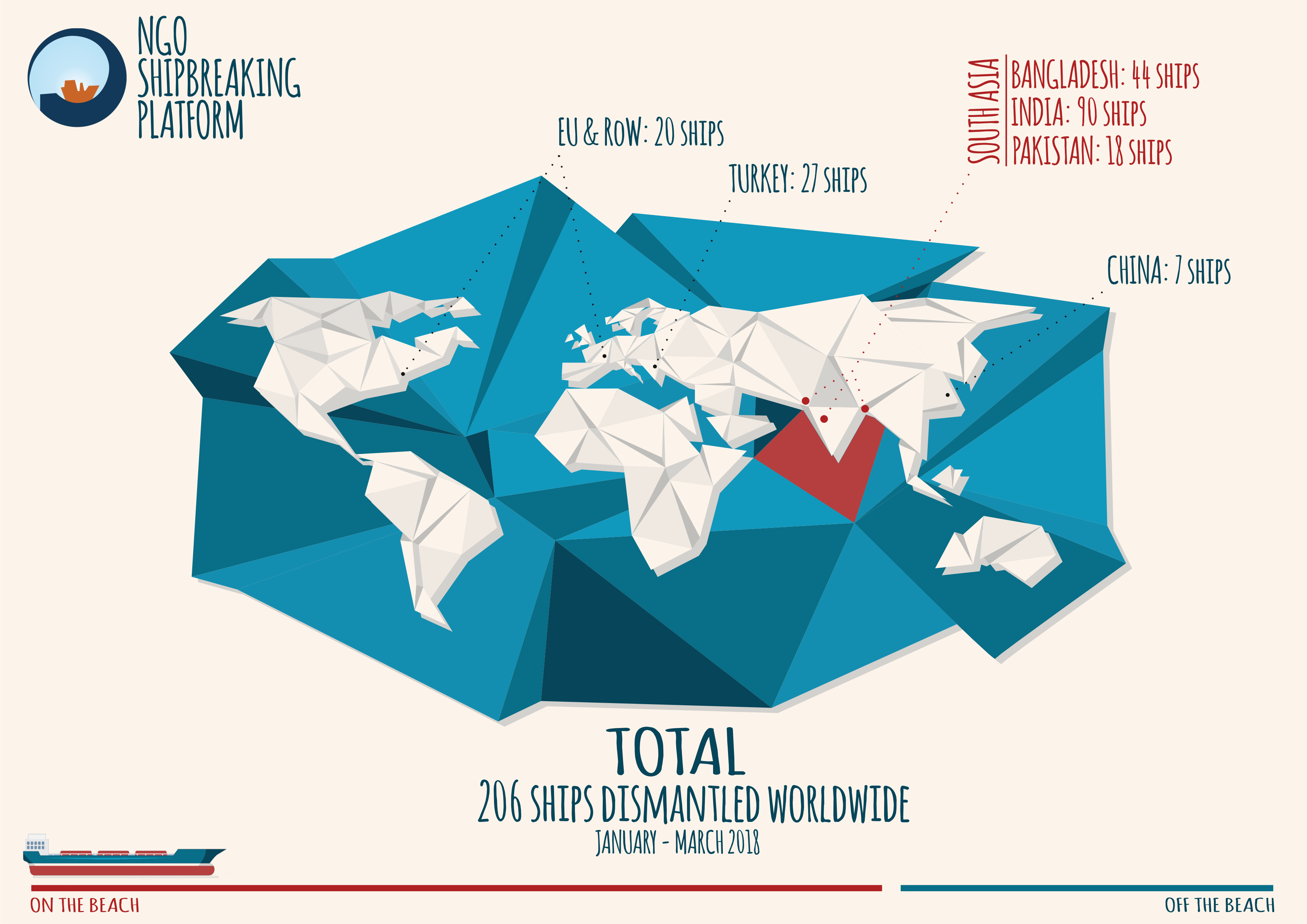
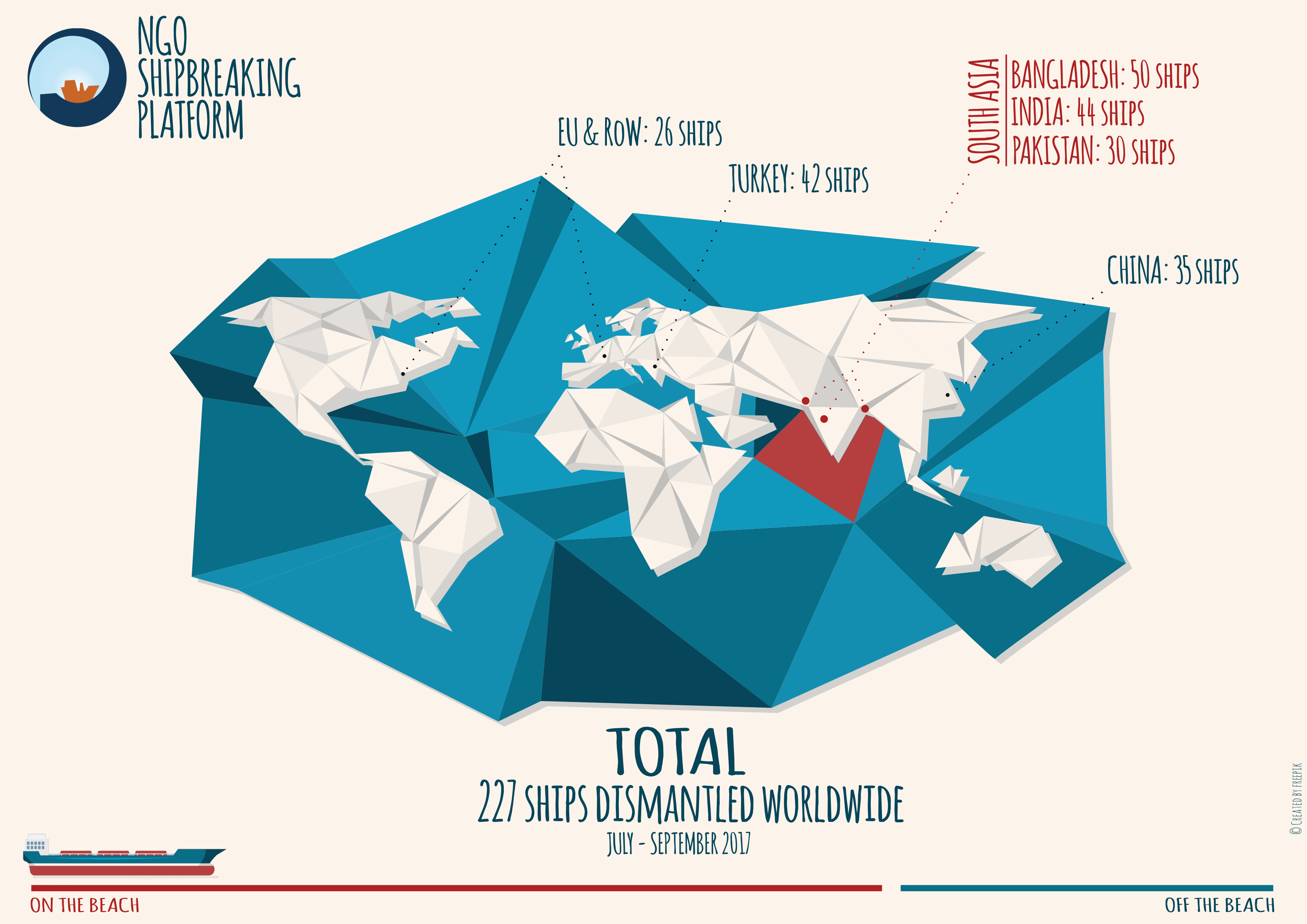
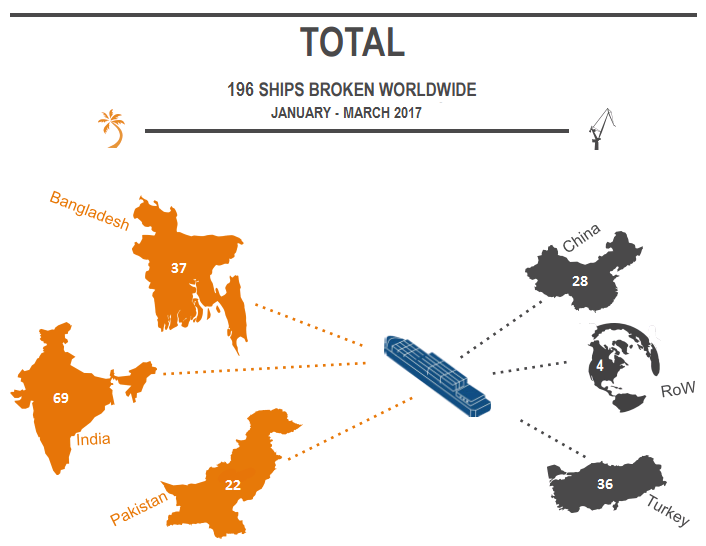
Despite the terrible accident that shook the international shipbreaking community in 2016, no lesson has been learned in Pakistan. In 2017, at least 10 workers lost their lives at the shipbreaking yards on the beach of Gadani. The Platform documented 15 deaths in the Bangladeshi yards last year, where also at least another 22 workers were seriously injured. Whilst international and local NGOs were repeatedly denied access to the Indian shipbreaking yards, the Platform was informed of at least eight fatal accidents in Alang in 2017.
DUMPERS 2017 - Worst practices
As in 2016, GERMANY and GREECE top the list of country dumpers in 2017. German owners, including banks and ship funds, beached 50 vessels out of a total of 53 sold for demolition. Greek owners were responsible for the highest absolute number of ships sold to South Asian shipbreaking yards in 2017: 51 ships in total. Since the Platform’s first compilation of data in 2009, Greek shipping companies have unceasingly topped the list of owners that opt for dirty and dangerous shipbreaking.
Despite increased pressure for safe and clean ship recycling from Norwegian investors and authorities, in 2017, the number of Norwegian-owned ships scrapped on the beach was on the rise: 16 ended up in Alang, Gadani and Chittagong. The attempted illegal export of the TIDE CARRIER to Pakistan was stopped by Norwegian authorities following an alert by the Platform.
“In light of increased pressure from Scandinavian banks and investors, including Norwegian pension funds KLP and NBIM, and ongoing criminal investigations against the owners of TIDE CARRIER, Norwegian ship owners will have to ask themselves whether dirty profits are worth the reputational and financial risk that using beaching facilities now entails. Also, Danish container-giant Maersk will have an increasingly hard time justifying its U-turn back to the beach in Alang, as the yards there will not make it on the EU list of approved ship recycling facilities [1]”, comments Ingvild Jenssen.
The worst corporate dumper prize goes to Continental Investment Holdings (CIH), the Singapore-headquartered shipowning arm of Myanmar shipowner Captain U Ko Ko Htoo and parent company of Continental Shipping Line. The company, which is currently changing the composition of its fleet, sold 9 ships for breaking on the beaches in 2017. Four vessels ended up in Bangladesh, where in late December, during the demolition of CIH’s TAUNG GYI STAR, a worker died hit by a falling iron plate.
Ranked at second place, the container shipping giant Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC) sold 7 vessels to Indian breakers. In the last nine years, MSC has profited from the sale of more than seventy ships for dirty and dangerous scrapping in Alang.
The Japanese owner Mitsui OSK Lines and the UK-based Zodiac Group follow closely with respectively 6 and 5 ships sold to South Asian yards. Zodiac received the worst dumper award in 2016 and sold 4 vessels to the yards in Chittagong despite being under scrutiny after a Bangladeshi worker sought compensation from the company for injuries incurred when breaking the EURUS LONDON.
Other known companies that in 2017 opted for substandard yards, rather than recycling their ships in a safe and clean manner, include: Hanjin Shipping, Hansa Mare Reederei, Peter Dohle Schiffahrts, Rickmers Reederei, Hansa Treuhand, Berge Bulk, Costamare, Quantum Pacific Group and Teekay. Teekay had promised to never sell to beaching yards again after a worker died breaking the ASPIRE in 2014 in Chittagong. That Berge Bulk was under the spotlight in December 2016, when it was feared that the Berge Stahl would end up on a beach, did not prevent the company from selling another 5 ships for dirty and dangerous breaking in 2017.
With the oil and gas sector seeing a downturn in the last couple of years, the Platform has documented an increase in offshore units that have gone for scrap. Out of the 91 units which have been identified as demolished in the last three years combined, 41 of them ended up on the beaches of South Asia after being towed for thousands of kilometers across the globe. Three floating platforms cold-stacked in Scotland that were sold by Diamond Offshore for scrap in 2017, allegedly to cash buyer GMS, were stopped from leaving following an alert by the Platform on their highly likely illegal export. “Fixed platforms cannot easily escape decommissioning rules, whereas we have seen that nearly half of all floating units slip under the radar and end up on beaches – this double standard has to stop”, states Francesca Carlsson, Corporate Liaison and Policy Officer of the NGO Shipbreaking Platform.
All vessels sold to the beaching yards pass through the hands of scrap dealers known as cash buyers. In this way, ship owners attempt to shield themselves from responsibility, and are paid upfront the highest market price in cash for their end-of-life vessels by the dealers. To reduce costs and to exploit the loopholes in international legislation, cash buyers will change a vessel’s flag to one of the typical last-voyage flags of convenience, such as Comoros, Palau and St Kitts and Nevis. Cash buyers will also register the vessel under a new name and a new post box company, rendering it very difficult for authorities to trace and hold cash buyers and ship owners accountable for illicit business practices.