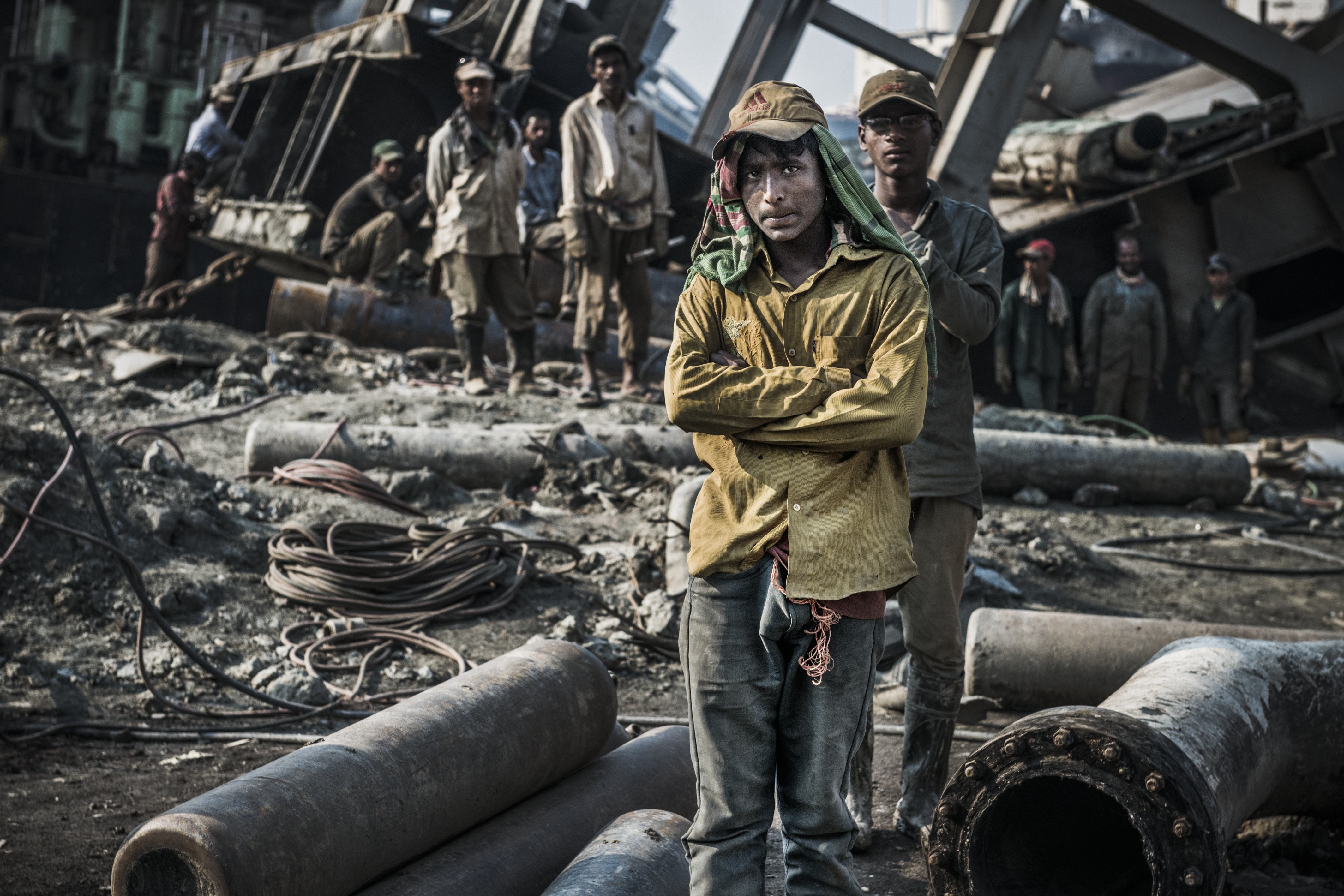
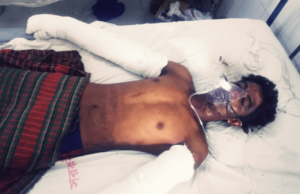
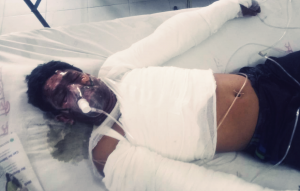
On 28 January, according to local sources, Md Motiur Rahman lost his life while working at S. S. Green Ship Breaking yard, located on the beach of Chittagong, Bangladesh. Twenty days later, a fire broke out in the engine room on board the Greek-owned Polembros’ tanker S WARRIOR at Shagorika Ship Breaking Yard, killing workers Md Jamil and Bipul.
No severe accidents were reported in India and Pakistan. Whilst information on accidents in Alang remain difficult to obtain due to lack of access and transparency, a significant decrease in scrapping activities has no doubt contributed to a quarter with no recorded accidents in Gadani. In the last six months, 70% of the workers are said to have lost their job.
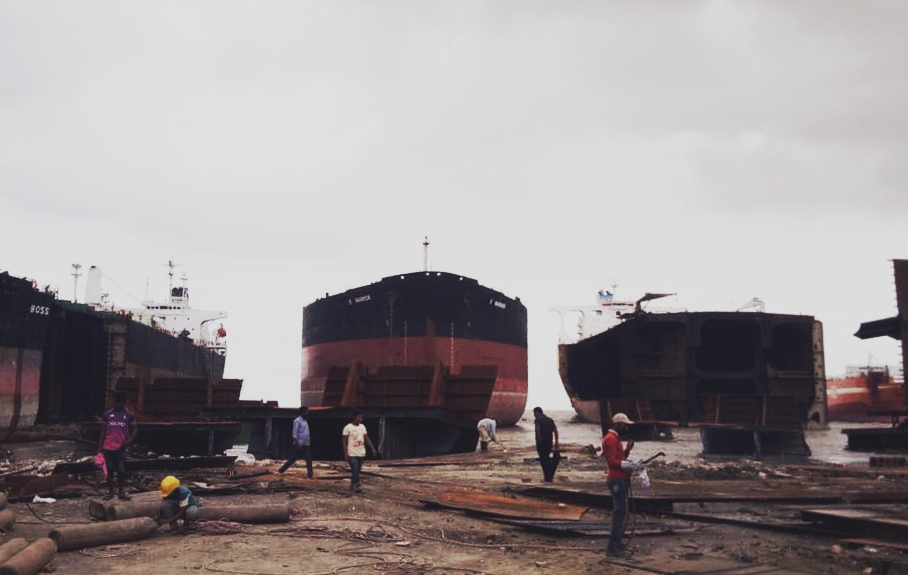
In the first quarter of 2019, US, Saudi Arabian and Singaporean ship owners sold the most ships to South Asian yards, followed by Greek and South Korean owners.
Data keep showing significant activity in the decommissioning of oil and gas units. At least 12 offshore assets reached the end of their lives in the first three months of this year. Transocean Ltd., based in Switzerland and listed on the New York Stock Exchange, is the offshore drilling contractor that scrapped most units in the last decade. Despite being under the spotlight for a series of accidents involving some of its drilling units [2], the company always distinguished itself for having adopted a good end-of-life fleet management policy that required the use of recycling yards that do not operate on tidal beaches. Regrettably, Transocean, however, recently took the decision to scrap its semi-submersible platform JACK BATES (IMO 8755780) on the beach of Alang, India. The platform was beached in February at R.K. Industries (Unit-II), one of the yards that are part of the Shree Ram Group. Shree Ram claims its yards are amongst the best facilities operating on the Alang beach. Ship owners, such as Danish Maersk, praise the company’s practices. However, past media reports and a recent inspection visit to one of its plots by the European Commission have flagged serious concerns related to e.g. pollution of the intertidal area, absence of medical facilities, breaches of labour rights and lack of capacity to manage certain hazardous wastes downstream. Indeed, the facility did not meet the safety and environmental requirements for EU approval and was thus not added to the EU list.
Norwegian Grieg Green, ship recycling consultancy fully owned by Grieg Star, facilitated the sale of the JACK BATES and will monitor the scrapping operations on the ground. This is the first time Grieg Green offers its expertise on a demolition project taking place on a South Asian beach. Whilst its parent company has recently hit the news for being one of the first ship owners to scrap a vessel responsibly under the new EU Ship Recycling Regulation at Leyal ship recycling yard in Turkey, Grieg Green seems to have abandoned the Grieg Group’s off the beach stance.
More than half of the ships sold to South Asia this quarter changed flag to the registries of Comoros, Niue, Palau and St. Kitts and Nevis just weeks before hitting the beach. All ships sold to the Chittagong, Alang and Gadani yards pass via the hands of scrap-dealers, also known as cash buyers, that often re-register and re-flag the vessel on its final voyage. Grey- and black-listed flags of convenience are particularly popular with cash buyers. These flags are not typically used during the operational life of ships and offer ‘last voyage registration’ discounts. They are grey- and black-listed due to their poor implementation of international maritime law. The high number of flag changes should alert authorities towards the ineffectiveness of legislation, including the EU Ship Recycling Regulation, which is based on flag state enforcement only.
The EU Ship Recycling Regulation became applicable on 1 January 2019. According to the Regulation, EU-flagged vessels have to be recycled in approved facilities included in the EU list. At least five ships were scrapped in accordance with the new requirements. However, the Platform recorded at least seven ships that swapped their European flag to that of a non-EU registry prior the last voyage to the shipbreaking yard in order to circumvent the legislation. Beaching yards do not feature on the EU list as they do not comply with the Regulation's requirements.
The case of the container ship BOXY LADY (IMO 9108386), owned by Greek Aims Shipping Corporation, illustrates how ship owners circumvent the law. In November 2018, the Platform alerted Spanish authorities about the imminent illegal export under the EU Waste Shipment Regulation of the Malta-flagged ship from the port of Vigo. Despite authorities having been informed, the vessel started its voyage towards Bangladesh. Aims Shipping Corporation then also managed to circumvent the EU Ship Recycling Regulation by changing the flag of the vessel to Bahamas in December 2018, just prior to its beaching in Chittagong in March.
The shipping industry claims that it is forced to re-flag as there is not enough capacity on the EU List. A report published in September last year by the NGO Shipbreaking Platform and Transport & Environment, however, showed that there was more than enough capacity, both in terms of tonnage and size, to cater for the EU flagged end-of-life fleet. Since then, two Turkish yards, a yard in the US and more European yards have been added to the list. This week the European Commission also announced that it intends to add a further eight yards operating in Denmark, Norway and Turkey to the List. Clearly, however, more efforts to detect violations of European waste law and stronger incentives, such as a return scheme for all vessels trading in the EU, are needed to ensure use of the EU list and proper enforcement of current legislation on ship recycling.