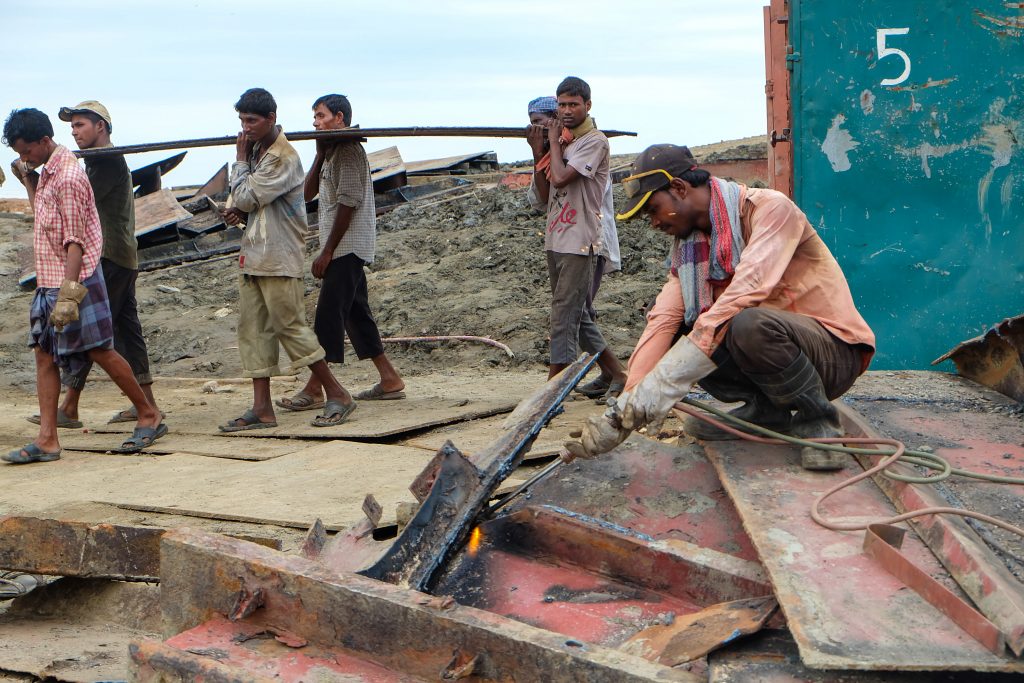
The Italian-flagged ferry MOBY DREA, which left Genoa in July after its owner assured Italian authorities it would be refurbished in Croatia and returned to service, is now mired in controversy. Following protests by Croatian civil society organisations, the heavily asbestos-contaminated vessel is again on the market for dismantling.
Public outrage in Split has been building for weeks, with the civic initiative “Zdravi Split” leading protests to demand that the ship leaves Croatia, as it was feared the removal of 400 tonnes of asbestos would be conducted locally at the Brodosplit yard, exposing workers and residents to unjustifiable risks. In response, Croatia’s Ministry of Sea, Transport, and Infrastructure ordered the vessel to leave within seven days, but later extended the deadline by fifteen. Now, it is reported that the ship is finally scheduled to depart today.
Open letters to the government stress that asbestos removal constitutes ship recycling, which is strictly regulated under EU law (Regulation 1257/2013) and the Basel Convention. The Brodosplit yard is not licensed for conducting scrapping operations, the ship should thus never have been allowed to enter Croatia in the first place.
Two official Inventories of Hazardous Materials dated 10 September 2024 and 20 January 2025 further eroded trust; the first having declared the presence of 64.30 tonnes of asbestos onboard, while the second estimating nearly 400 tonnes. This huge discrepancy raises serious concerns about oversight and transparency, and adds to the sense that the MOBY DREA case has been mishandled from the outset.

The Platform warns that Turkey, a likely destination for scrapping, cannot be considered a responsible option. Turkish ship recycling yards have repeatedly been criticised for unsafe practices, particularly in the handling and disposal of toxics such as asbestos. Sending a vessel with nearly 400 tonnes of asbestos to such facilities would endanger the health of workers and surrounding communities.